[TOC]
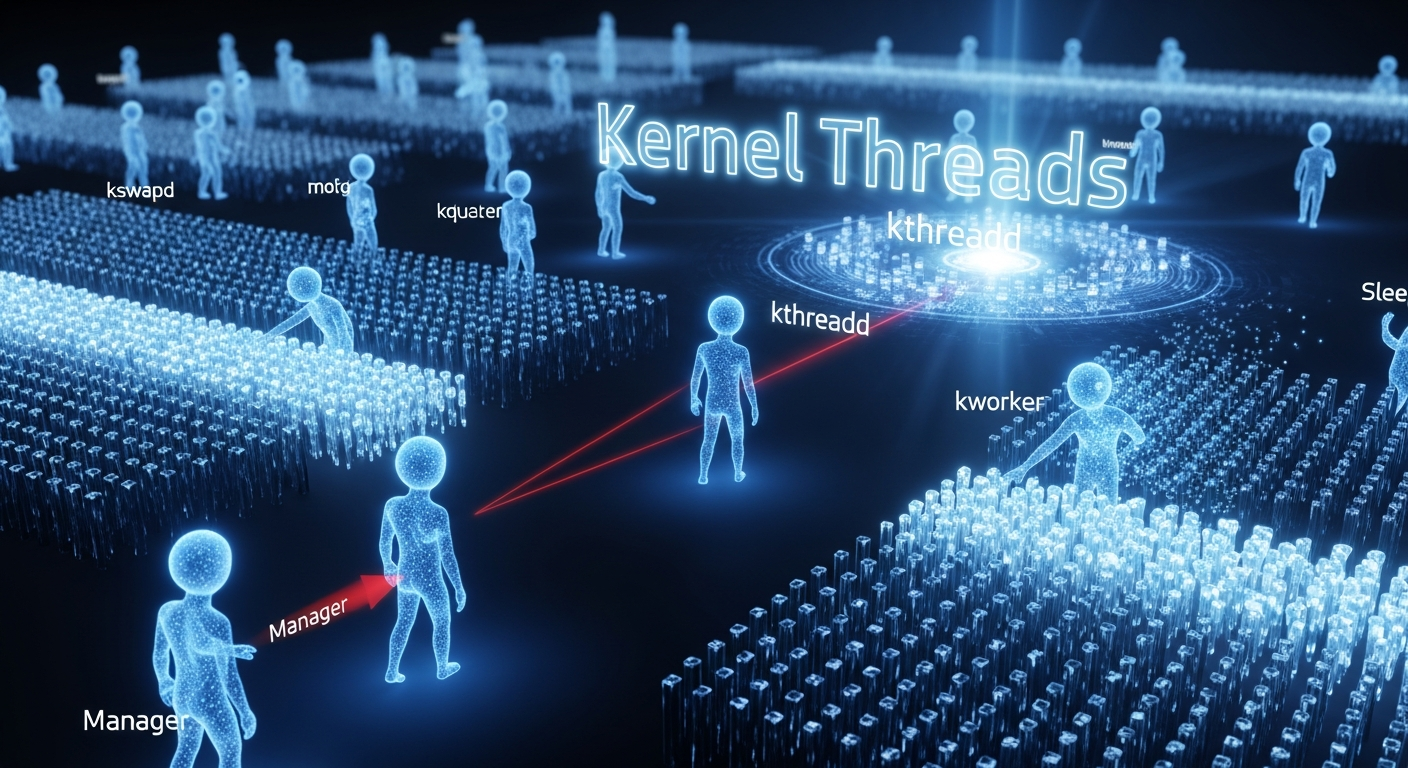
kernel/kthread.c 内核线程(Kernel Threads) 内核后台任务的创建与管理 历史与背景 这项技术是为了解决什么特定问题而诞生的? kernel/kthread.c 提供的内核线程(kthread)机制是为了解决内核自身需要执行长时间运行的、可阻塞的后台任务 这一根本需求而诞生的。
在内核中,许多任务不能在任何用户进程的上下文中执行,也不能在中断上下文中完成。
中断上下文的局限性 :中断处理程序(包括softirq/tasklet)必须快速执行且绝对不能睡眠(阻塞)。然而,很多内核任务需要进行I/O操作、获取信号量或等待定时器,这些都会导致睡眠。用户进程上下文的不可靠性 :内核的后台任务(如刷新脏页到磁盘、管理内存)必须在系统的整个生命周期中持续运行。如果将这些任务依附于某个用户进程,那么当该进程退出或被杀死时,这些关键的内核任务也将终止,这是不可接受的。
kthread就是为了提供一个纯粹的、独立的内核执行上下文 而设计的。它是一个在内核空间运行、没有用户地址空间(mm_struct)的特殊“进程”。这使得内核可以创建自己的“守护进程(daemons)”,这些守护进程可以被调度、可以睡眠、可以执行任何需要在进程上下文中完成的操作,同时其生命周期完全由内核控制。
它的发展经历了哪些重要的里程碑或版本迭代?
早期的kernel_thread() :在kthread API出现之前,内核使用一个名为kernel_thread()的函数来创建内核线程。这个接口功能较为原始,需要手动进行许多设置。标准化的kthread_* API :一个重要的里程碑是引入了一套以kthread_为前缀的、更加健壮和易用的API。这包括:
kthread_create(): 只创建线程,不运行。kthread_run(): 创建并立即运行线程。kthread_stop(): 一个设计精良的、同步的线程停止机制,它会向线程发出停止请求,并等待其真正退出。
与Freezer的集成 :为了支持系统挂起/休眠(Suspend/Hibernate),内核线程需要能够被“冻结(freeze)”。kthread框架与内核的freezer机制紧密集成,允许kthreads在系统进入休眠状态时安全地暂停。Per-CPU线程的简化 :为在每个CPU上都运行一个实例的常见模式提供了辅助函数,简化了这类线程的创建和管理。
目前该技术的社区活跃度和主流应用情况如何? kthread是内核最基础、最稳定的基础设施之一。其核心API很少变动,社区的活跃度主要体现在内核的各个子系统如何使用它来构建自己的后台任务。
kswapdkworkerkworker这些内核线程中执行的。文件系统日志线程 :如ext4的jbd2线程,负责将文件系统日志提交到磁盘。CPU调度相关线程 :如用于CPU间任务迁移的migration线程,以及用于负载均衡的调度器线程。
核心原理与设计 它的核心工作原理是什么? kthread的核心原理是利用clone()系统调用的底层机制,创建一个不与用户空间关联的、只在内核态运行 的新任务(task_struct)。
创建过程 :
当驱动程序调用kthread_create()时,内核会准备一个kthread_create_info结构体,其中包含了用户提供的线程函数、参数等信息。
然后,它会调用kernel_clone()(这是_do_fork的一个封装)。在调用kernel_clone()时,会传入CLONE_KERNEL等特殊标志,但不会 传入CLONE_VM。
这意味着新创建的任务会获得一个独立的task_struct ,但它不会复制父进程的用户地址空间,而是将其mm和active_mm字段指向NULL,表示它没有自己的用户空间。
启动与执行 :
新创建的kthread并不会直接从用户提供的函数开始执行,而是从一个通用的包装函数kthread()开始。
kthread()函数负责进行一些初始化,如屏蔽所有信号,然后才调用用户传入的真正线程函数。
线程主循环 :
一个设计良好的kthread,其主函数通常是一个while循环。循环的条件是!kthread_should_stop()。
在循环内部,线程执行其具体任务,并在任务间歇调用schedule()、msleep()或在等待队列上等待,以让出CPU。
停止机制 (kthread_stop) :
当其他代码调用kthread_stop()时,它会首先设置kthread_should_stop()将返回true的标志。
然后,它会唤醒正在睡眠的目标kthread。
被唤醒的kthread在下一次循环检查时,发现kthread_should_stop()为真,于是跳出循环,执行清理工作并返回。
kthread_stop()函数会一直等待,直到目标kthread完全退出,这是一个同步的、确保资源被完全释放的操作。
它的主要优势体现在哪些方面?
拥有进程上下文 :这是kthread最核心的优势。因为它是一个完整的、可调度的任务,所以它可以睡眠(阻塞) 。这使得它可以执行等待I/O、获取mutex等操作。独立的生命周期 :kthread的生命周期完全由内核代码控制,独立于任何用户进程,保证了内核关键任务的持续运行。可调度性 :作为标准的task_struct,kthread可以被赋予不同的调度策略和优先级,允许内核对后台任务进行精细的性能控制。安全的退出机制 :kthread_stop()提供了一个清晰、无竞态的范式来安全地终止线程。
它存在哪些已知的劣势、局限性或在特定场景下的不适用性?
开销相对较大 :与workqueue或tasklet相比,创建一个完整的task_struct来代表一个kthread,其内存和调度器开销更大。因此,它不适合用于执行大量、短小的“一次性”任务。编程模型更复杂 :开发者需要自己管理线程的主循环、睡眠/唤醒逻辑以及对kthread_should_stop()的检查。而workqueue模型则简单得多,只需提供一个函数即可。
使用场景 在哪些具体的业务或技术场景下,它是首选解决方案? kthread是那些需要长期运行、周期性执行或需要在后台等待事件的内核任务 的首选。
周期性轮询 :一个驱动需要每隔500毫秒检查一次硬件状态。可以创建一个kthread,其主循环中包含一个msleep(500)。内核守护进程 :如上文提到的kswapd,它大部分时间都在等待队列上睡眠,只有在内存压力达到阈值时才被唤醒执行工作。阻塞式I/O处理 :一个内核任务需要将大量数据写入磁盘。它可以创建一个kthread来执行这个写操作,因为写磁盘是一个阻塞操作。
是否有不推荐使用该技术的场景?为什么?
短小的、一次性的延迟任务 :如果只是想把一个简短的任务从中断上下文推迟到进程上下文执行,应该使用**workqueue**。例如,在中断处理程序中检测到一个设备状态改变,需要执行一些不紧急的后续处理。为这种任务创建一个完整的kthread然后销毁它,效率太低。高性能、高频率的延迟任务(不睡眠) :如果延迟的任务非常短小、执行频率非常高,且不需要睡眠,那么tasklet是比kthread更轻量、更高效的选择。
对比分析 请将其 与 其他相似技术 进行详细对比。
特性
内核线程 (Kthread)
工作队列 (Workqueue)
任务队列 (Tasklet) / 软中断 (Softirq)
执行上下文 进程上下文 进程上下文 中断上下文 (软中断)
能否睡眠 可以 可以 绝对不能
生命周期 长周期 。通常用于创建守护进程,与系统共存。短周期 。为“一次性”的延迟任务设计。极短周期 。为中断的下半部设计。
创建开销 高 。需要创建完整的task_struct。低 。只需创建一个work_struct并将其排入共享的kworker线程。极低/静态 。
编程模型 复杂 。开发者需手动管理线程主循环和退出逻辑。简单 。只需提供一个函数,然后调用queue_work()。简单 。只需提供一个函数,然后调用tasklet_schedule()。
主要用途 内核守护进程、周期性任务、需要独立调度实体的后台工作。
将工作从中断上下文或其他不允许睡眠的地方推迟执行。这是最常用 的延迟执行机制。
中断处理的下半部,用于高性能、不睡眠的延迟任务。
include/linux/kthread.h kthread_init_work 初始化工作线程 将工作线程的结构体初始化为零,并设置函数指针 1 2 3 4 5 6 #define kthread_init_work(work, fn) \ do { \ memset((work), 0, sizeof(struct kthread_work)); \ INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(work)->node); \ (work)->func = (fn); \ } while (0)
kthread_init_worker 初始化工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 #define kthread_init_worker(worker) \ do { \ static struct lock_class_key __key; \ __kthread_init_worker((worker), "(" #worker")->lock" , &__key); \ } while (0)
kthread_create_worker 创建工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 __printf(3 , 4 ) struct kthread_worker *kthread_create_worker_on_node (unsigned int flags, int node, const char namefmt[], ...) ;#define kthread_create_worker(flags, namefmt, ...) \ kthread_create_worker_on_node(flags, NUMA_NO_NODE, namefmt, ## __VA_ARGS__);
kthread_run_worker 创建并唤醒 kthread worker 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #define kthread_run_worker(flags, namefmt, ...) \ ({ \ struct kthread_worker *__kw \ = kthread_create_worker(flags, namefmt, ## __VA_ARGS__); \ if (!IS_ERR(__kw)) \ wake_up_process(__kw->task); \ __kw; \ })
kernel/kthread.c to_kthread 检查内核线程,返回kthread结构体指针
检查传入的任务是否是一个内核线程(kernel thread),并返回与该任务关联的 kthread 结构体指针
1 2 3 4 5 static inline struct kthread *to_kthread (struct task_struct *k) { WARN_ON(!(k->flags & PF_KTHREAD)); return k->worker_private; }
set_kthread_struct 设置线程结构体 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 bool set_kthread_struct (struct task_struct *p) { struct kthread *kthread ; if (WARN_ON_ONCE(to_kthread(p))) return false ; kthread = kzalloc(sizeof (*kthread), GFP_KERNEL); if (!kthread) return false ; init_completion(&kthread->exited); init_completion(&kthread->parked); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&kthread->hotplug_node); p->vfork_done = &kthread->exited; kthread->task = p; kthread->node = tsk_fork_get_node(current); p->worker_private = kthread; return true ; }
__kthread_init_worker 初始化工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void __kthread_init_worker(struct kthread_worker *worker, const char *name, struct lock_class_key *key) { memset (worker, 0 , sizeof (struct kthread_worker)); raw_spin_lock_init(&worker->lock); lockdep_set_class_and_name(&worker->lock, key, name); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&worker->work_list); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&worker->delayed_work_list); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(__kthread_init_worker);
__kthread_create_on_node 创建内核线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 struct task_struct *__kthread_create_on_node (int (*threadfn )(void *data ), void *data , int node , const char namefmt [], va_list args ) { DECLARE_COMPLETION_ONSTACK(done); struct task_struct *task ; struct kthread_create_info *create =sizeof (*create), GFP_KERNEL); if (!create) return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); create->threadfn = threadfn; create->data = data; create->node = node; create->done = &done; create->full_name = kvasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, namefmt, args); if (!create->full_name) { task = ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); goto free_create; } spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock); list_add_tail(&create->list , &kthread_create_list); spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock); wake_up_process(kthreadd_task); if (unlikely(wait_for_completion_killable(&done))) { if (xchg(&create->done, NULL )) return ERR_PTR(-EINTR); wait_for_completion(&done); } task = create->result; free_create: kfree(create->full_name); kfree(create); return task; }
kthread_create_on_node 创建内核线程,调用传入的线程函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 struct task_struct *kthread_create_on_node (int (*threadfn)(void *data), void *data, int node, const char namefmt[], ...) { struct task_struct *task ; va_list args; va_start(args, namefmt); task = __kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, node, namefmt, args); va_end(args); return task; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_create_on_node);
kthread_worker_fn 处理kthread_worker的kthread函数
它的核心作用是:在一个无限循环中,不断地从其私有的工作链表(工人->工作列表)中取出待处理的工作项(线程工作),并串行地执行它们。当没有工作时,它会进入可中断睡眠,直到被kthread_queue_work唤醒。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 int kthread_worker_fn (void *worker_ptr) { struct kthread_worker *worker = struct kthread_work *work ; WARN_ON(worker->task && worker->task != current); worker->task = current; if (worker->flags & KTW_FREEZABLE) set_freezable(); repeat: set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); if (kthread_should_stop()) { __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); raw_spin_lock_irq(&worker->lock); worker->task = NULL ; raw_spin_unlock_irq(&worker->lock); return 0 ; } work = NULL ; raw_spin_lock_irq(&worker->lock); if (!list_empty(&worker->work_list)) { work = list_first_entry(&worker->work_list, struct kthread_work, node); list_del_init(&work->node); } worker->current_work = work; raw_spin_unlock_irq(&worker->lock); if (work) { kthread_work_func_t func = work->func; __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); trace_sched_kthread_work_execute_start(work); work->func(work); trace_sched_kthread_work_execute_end(work, func); } else if (!freezing(current)) { schedule(); } else { __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); } try_to_freeze(); cond_resched(); goto repeat; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kthread_worker_fn);
kthread_create_worker_on_node 创建内核线程工作,调用内核工作函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 static __printf(3 , 0 ) struct kthread_worker *__kthread_create_worker_on_node (unsigned int flags , int node , const char namefmt [], va_list args ) { struct kthread_worker *worker ; struct task_struct *task ; worker = kzalloc(sizeof (*worker), GFP_KERNEL); if (!worker) return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); kthread_init_worker(worker); task = __kthread_create_on_node(kthread_worker_fn, worker, node, namefmt, args); if (IS_ERR(task)) goto fail_task; worker->flags = flags; worker->task = task; return worker; fail_task: kfree(worker); return ERR_CAST(task); } struct kthread_worker *kthread_create_worker_on_node (unsigned int flags, int node, const char namefmt[], ...) { struct kthread_worker *worker ; va_list args; va_start(args, namefmt); worker = __kthread_create_worker_on_node(flags, node, namefmt, args); va_end(args); return worker; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_create_worker_on_node);
kthread_bind 将内核线程绑定到特定的CPU 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 static void __kthread_bind_mask(struct task_struct *p, const struct cpumask *mask, unsigned int state){ unsigned long flags; if (!wait_task_inactive(p, state)) { WARN_ON(1 ); return ; } raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&p->pi_lock, flags); do_set_cpus_allowed(p, mask); p->flags |= PF_NO_SETAFFINITY; raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&p->pi_lock, flags); } static void __kthread_bind(struct task_struct *p, unsigned int cpu, unsigned int state){ __kthread_bind_mask(p, cpumask_of(cpu), state); } void kthread_bind_mask (struct task_struct *p, const struct cpumask *mask) { struct kthread *kthread = __kthread_bind_mask(p, mask, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE); WARN_ON_ONCE(kthread->started); } void kthread_bind (struct task_struct *p, unsigned int cpu) { struct kthread *kthread = __kthread_bind(p, cpu, TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE); WARN_ON_ONCE(kthread->started); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_bind);
kthread_create_on_cpu 创建一个绑定到特定CPU的内核线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 struct task_struct *kthread_create_on_cpu (int (*threadfn)(void *data), void *data, unsigned int cpu, const char *namefmt) { struct task_struct *p ; p = kthread_create_on_node(threadfn, data, cpu_to_node(cpu), namefmt, cpu); if (IS_ERR(p)) return p; kthread_bind(p, cpu); to_kthread(p)->cpu = cpu; return p; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_create_on_cpu);
create_kthread 负责执行实际的线程创建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 static void create_kthread (struct kthread_create_info *create) { int pid; #ifdef CONFIG_NUMA current->pref_node_fork = create->node; #endif pid = kernel_thread(kthread, create, create->full_name, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES | SIGCHLD); if (pid < 0 ) { struct completion *done =NULL ); kfree(create->full_name); if (!done) { kfree(create); return ; } create->result = ERR_PTR(pid); complete(done); } }
kthreadd 所有内核线程的管理器线程的主函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 int kthreadd (void *unused) { static const char comm[TASK_COMM_LEN] = "kthreadd" ; struct task_struct *tsk = set_task_comm(tsk, comm); ignore_signals(tsk); set_cpus_allowed_ptr(tsk, housekeeping_cpumask(HK_TYPE_KTHREAD)); set_mems_allowed(node_states[N_MEMORY]); current->flags |= PF_NOFREEZE; cgroup_init_kthreadd(); for (;;) { set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE); if (list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) schedule(); __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock); while (!list_empty(&kthread_create_list)) { struct kthread_create_info *create ; create = list_entry(kthread_create_list.next, struct kthread_create_info, list ); list_del_init(&create->list ); spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock); create_kthread(create); spin_lock(&kthread_create_lock); } spin_unlock(&kthread_create_lock); } return 0 ; }
__kthread_parkme 为内核线程提供一个标准的“停泊(Parking)”机制
它的核心作用是为内核线程提供一个标准的“停泊(Parking)”机制。 当其他内核代码(通常是该线程的创建者或管理者)请求一个内核线程暂停其工作时,该线程会在__kthread_parkme这里进入睡眠,直到被明确地“唤醒(unpark)”。..
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 static void __kthread_parkme(struct kthread *self){ for (;;) { set_special_state(TASK_PARKED); if (!test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_PARK, &self->flags)) break ; preempt_disable(); complete(&self->parked); schedule_preempt_disabled(); preempt_enable(); } __set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING); }
kthread_park 停泊一个由kthread_create()创建的线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 int kthread_park (struct task_struct *k) { struct kthread *kthread = if (WARN_ON(k->flags & PF_EXITING)) return -ENOSYS; if (WARN_ON_ONCE(test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_PARK, &kthread->flags))) return -EBUSY; set_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_PARK, &kthread->flags); if (k != current) { wake_up_process(k); wait_for_completion(&kthread->parked); WARN_ON_ONCE(!wait_task_inactive(k, TASK_PARKED)); } return 0 ; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kthread_park);
kthread_unpark 清除目标内核线程k的“应该停泊”标志,并将其从特殊的TASK_PARKED睡眠状态中唤醒,使其能够继续执行 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 void kthread_unpark (struct task_struct *k) { struct kthread *kthread = if (!test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_PARK, &kthread->flags)) return ; if (test_bit(KTHREAD_IS_PER_CPU, &kthread->flags)) __kthread_bind(k, kthread->cpu, TASK_PARKED); clear_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_PARK, &kthread->flags); wake_up_state(k, TASK_PARKED); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kthread_unpark);
kthread 所有新内核线程的入口包装函数
它是所有通过kthread_create()系列函数创建的内核线程,在被kthreadd派生(fork)出来后,第一个真正执行的C函数。它是一个通用的“外壳”或“启动器”
kthread函数是新创建的内核线程的通用入口点。它并不执行用户指定的具体任务,而是负责在新线程的上下文中,完成一系列关键的初始化、同步和生命周期管理工作,然后才调用用户提供的线程主函数(threadfn)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 static int kthread (void *_create) { static const struct sched_param param =0 }; struct kthread_create_info *create = int (*threadfn)(void *data) = create->threadfn; void *data = create->data; struct completion *done ; struct kthread *self ; int ret; self = to_kthread(current); done = xchg(&create->done, NULL ); if (!done) { kfree(create->full_name); kfree(create); kthread_exit(-EINTR); } self->full_name = create->full_name; self->threadfn = threadfn; self->data = data; sched_setscheduler_nocheck(current, SCHED_NORMAL, ¶m); __set_current_state(TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE); create->result = current; preempt_disable(); complete(done); schedule_preempt_disabled(); preempt_enable(); self->started = 1 ; if (!(current->flags & PF_NO_SETAFFINITY) && !self->preferred_affinity) kthread_affine_node(); ret = -EINTR; if (!test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &self->flags)) { __kthread_parkme(self); ret = threadfn(data); } kthread_exit(ret); }
kthread_exit 结束内核线程的生命周期 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 void __noreturn kthread_exit (long result) { struct kthread *kthread = kthread->result = result; if (!list_empty(&kthread->hotplug_node)) { mutex_lock(&kthreads_hotplug_lock); list_del(&kthread->hotplug_node); mutex_unlock(&kthreads_hotplug_lock); if (kthread->preferred_affinity) { kfree(kthread->preferred_affinity); kthread->preferred_affinity = NULL ; } } do_exit(0 ); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_exit);
kthread_should_stop 检查当前内核线程是否应该停止 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 bool kthread_should_stop (void ) { return test_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &to_kthread(current)->flags); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_should_stop);
kthread_stop 请求一个指定的内核线程k停止 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 int kthread_stop (struct task_struct *k) { struct kthread *kthread ; int ret; trace_sched_kthread_stop(k); get_task_struct(k); kthread = to_kthread(k); set_bit(KTHREAD_SHOULD_STOP, &kthread->flags); kthread_unpark(k); set_tsk_thread_flag(k, TIF_NOTIFY_SIGNAL); wake_up_process(k); wait_for_completion(&kthread->exited); ret = kthread->result; put_task_struct(k); trace_sched_kthread_stop_ret(ret); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_stop);
kthread_stop_put 停止一个内核线程并释放其task_struct 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int kthread_stop_put (struct task_struct *k) { int ret; ret = kthread_stop(k); put_task_struct(k); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(kthread_stop_put);
kthread_queue_work 将一个kthread_work排入队列
它的核心作用是:将一个指定的工作项(struct kthread_work)安全地、原子性地排入一个特定的kthread工作者(struct kthread_worker)的待办事项链表中,并唤醒该工作者线程(如果它在睡眠)来处理这个工作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 static inline bool queuing_blocked (struct kthread_worker *worker, struct kthread_work *work) { lockdep_assert_held(&worker->lock); return !list_empty(&work->node) || work->canceling; } static void kthread_insert_work (struct kthread_worker *worker, struct kthread_work *work, struct list_head *pos) { kthread_insert_work_sanity_check(worker, work); trace_sched_kthread_work_queue_work(worker, work); list_add_tail(&work->node, pos); work->worker = worker; if (!worker->current_work && likely(worker->task)) wake_up_process(worker->task); } bool kthread_queue_work (struct kthread_worker *worker, struct kthread_work *work) { bool ret = false ; unsigned long flags; raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&worker->lock, flags); if (!queuing_blocked(worker, work)) { kthread_insert_work(worker, work, &worker->work_list); ret = true ; } raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&worker->lock, flags); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(kthread_queue_work);
kthread_set_per_cpu 为一个内核线程设置其per-cpu身份和关联的CPU 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 void kthread_set_per_cpu (struct task_struct *k, int cpu) { struct kthread *kthread = if (!kthread) return ; WARN_ON_ONCE(!(k->flags & PF_NO_SETAFFINITY)); if (cpu < 0 ) { clear_bit(KTHREAD_IS_PER_CPU, &kthread->flags); return ; } kthread->cpu = cpu; set_bit(KTHREAD_IS_PER_CPU, &kthread->flags); }
kthreads_init 初始化kthread子系统 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 static int kthreads_init (void ) { return cpuhp_setup_state(CPUHP_AP_KTHREADS_ONLINE, "kthreads:online" , kthreads_online_cpu, NULL ); }