[TOC]

tinyuz\compress\tuz_enc.cpp
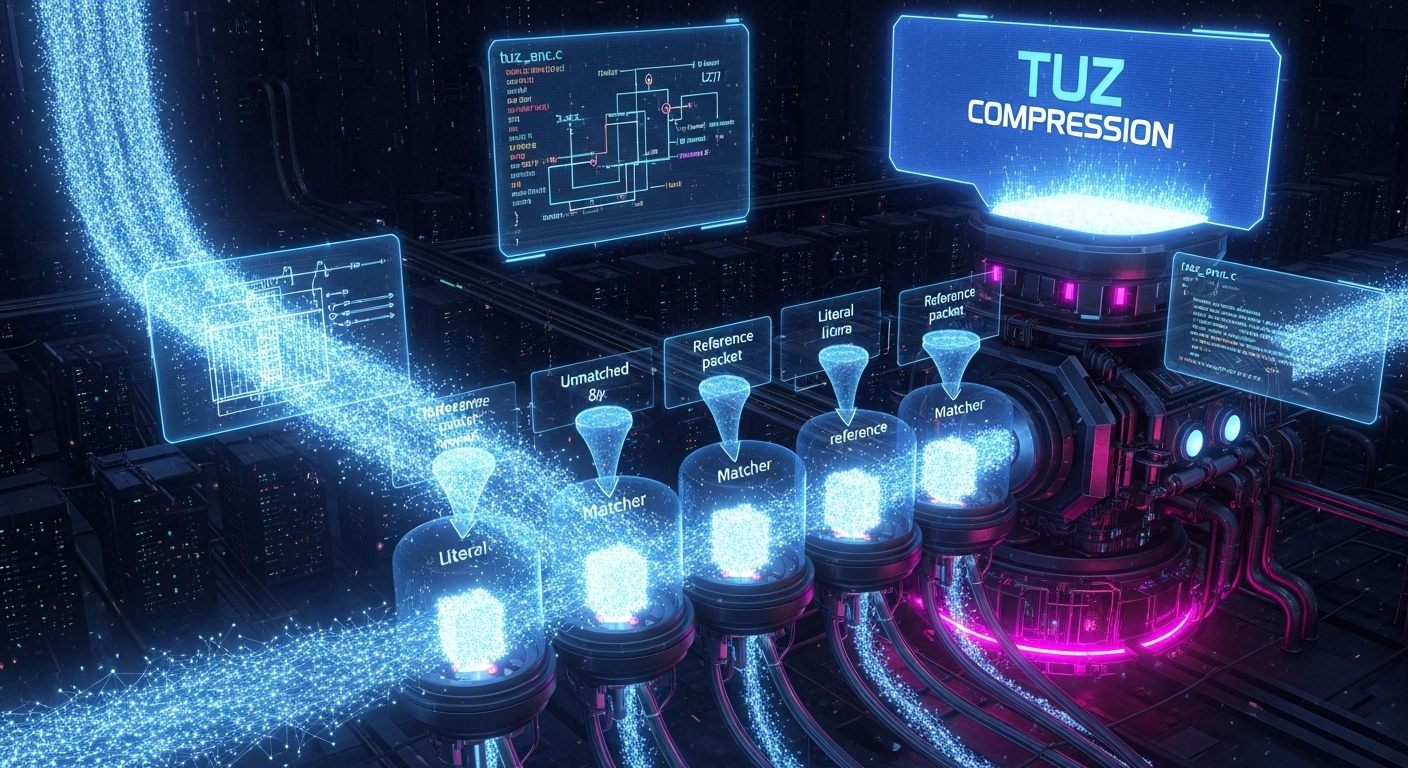
tuz_compress Tuz 数据压缩核心实现
- 负责执行 Tuz 无损压缩算法,将输入数据流 (
data) 压缩后写入输出数据流 (out_code)。该实现同时支持高效的单线程和多线程压缩模式。
原理与设计思路解析
tuz_compress 函数是 Tuz 压缩器的核心,它负责编排整个压缩流程。其设计思想围绕着分块处理 (Clipping) 和并行计算,以在处理大规模数据时兼顾内存效率和执行速度。
代码解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
|
hpatch_StreamPos_t tuz_compress(const hpatch_TStreamOutput* out_code,const hpatch_TStreamInput* data,
const tuz_TCompressProps* props){
checkv(out_code&&(out_code->write));
checkv(data&&(data->read));
if (props){
checkv((props->dictSize>=1)&(props->dictSize<=tuz_kMaxOfDictSize));
checkv(props->dictSize==(tuz_size_t)props->dictSize);
checkv(props->maxSaveLength==(tuz_length_t)props->maxSaveLength);
checkv((props->maxSaveLength>=tuz_kMinOfMaxSaveLength)&&(props->maxSaveLength<=tuz_kMaxOfMaxSaveLength));
}
tuz_TCompressProps selfProps=(props)?*props:tuz_kDefaultCompressProps;
if (selfProps.dictSize>data->streamSize){
selfProps.dictSize=(size_t)(data->streamSize);
if (selfProps.dictSize==0)
selfProps.dictSize=1;
}
hpatch_StreamPos_t cur_out_pos=0;
std::vector<tuz_byte> code;
{
assert(code.empty());
TTuzCode coder(code,selfProps.isNeedLiteralLine);
checkv(selfProps.dictSize==(tuz_size_t)selfProps.dictSize);
checkv(selfProps.maxSaveLength==(tuz_length_t)selfProps.maxSaveLength);
coder.outDictSize(selfProps.dictSize);
_flush_code(out_code,cur_out_pos,code);
}
size_t curDictSizeMax=tuz_kMinOfDictSize;
hpatch_StreamPos_t clipSize;
size_t threadNum=(props)?props->threadNum:1;
{
clipSize=((hpatch_StreamPos_t)selfProps.dictSize+1)/3;
if (clipSize<kMinBestClipSize) clipSize=kMinBestClipSize;
if (clipSize>kMaxBestClipSize) clipSize=kMaxBestClipSize;
hpatch_StreamPos_t clipCount=(data->streamSize+clipSize)/clipSize;
clipSize=(data->streamSize+clipCount-1)/clipCount;
if (threadNum>clipCount) threadNum=(size_t)clipCount;
}
#if (_IS_USED_MULTITHREAD)
if (threadNum>1){
TMt mt(out_code,data);
mt.selfProps=selfProps;
mt.clipSize=clipSize;
mt.curWorkClipPos=0;
mt.curOutedClipPos=0;
mt.curWritePos=cur_out_pos;
mt.curDictSizeMax=curDictSizeMax;
mt.workBufList=0;
std::vector<TWorkBuf> _codeList;
_codeList.resize(threadNum+1+threadNum/2);
for (size_t i=0;i<_codeList.size();++i)
checkv(mt.work_chan.send(&_codeList[i],true));
mt.start_threads((int)threadNum,_tuz_compress_mt,&mt,true);
mt.wait_all_thread_end();
checkv(!mt.is_on_error());
checkv(mt.curOutedClipPos==data->streamSize);
curDictSizeMax=mt.curDictSizeMax;
cur_out_pos=mt.curWritePos;
}else
#endif
{
TDictBuf dict_buf;
for (hpatch_StreamPos_t clipBegin=0;true;clipBegin+=clipSize) {
hpatch_StreamPos_t clipEnd=clipBegin+clipSize;
bool isToStreamEnd=(clipEnd>=data->streamSize);
if (isToStreamEnd) clipEnd=data->streamSize;
assert(code.empty());
TTuzCode coder(code,selfProps.isNeedLiteralLine);
if (clipBegin<clipEnd){
compress_clip(coder,data,clipBegin,clipEnd,selfProps,dict_buf);
}
if (!isToStreamEnd)
coder.outCtrl_clipEnd();
else
coder.outCtrl_streamEnd();
curDictSizeMax=std::max(curDictSizeMax,coder.getCurDictSizeMax());
_flush_code(out_code,cur_out_pos,code);
if (isToStreamEnd) break;
}
}
{
checkv(curDictSizeMax<=selfProps.dictSize);
if (curDictSizeMax<selfProps.dictSize){
assert(code.empty());
TTuzCode coder(code,selfProps.isNeedLiteralLine);
coder.outDictSize(curDictSizeMax);
hpatch_StreamPos_t dict_out_pos=0;
_flush_code(out_code,dict_out_pos,code);
}
}
return cur_out_pos;
}
|
tinyuz\compress\tuz_enc_private\tuz_enc_clip.cpp
compress_clip Tuz 数据块压缩核心逻辑
- 作为
tuz_compress 调用的核心工作函数,负责对单个数据块(clip)执行实际的 LZ77-style 压缩算法。
原理与设计思路解析
compress_clip 函数是 Tuz 压缩算法的心脏。它接收一个明确的数据范围(clipBegin 到 clipEnd),并利用一个“滑动窗口”(由 TDictBuf 维护)作为字典来查找和编码重复的数据序列。
代码解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
| namespace _tuz_private{
static void _outData(const tuz_byte* back,size_t unmatched_len,
_tuz_private::TTuzCode& coder,const tuz_TCompressProps& props){
while (unmatched_len){
size_t len=(unmatched_len<=props.maxSaveLength)?unmatched_len:props.maxSaveLength;
coder.outData(back,back+len);
back+=len;
unmatched_len-=len;
}
}
void compress_clip(TTuzCode& coder,const hpatch_TStreamInput* data,hpatch_StreamPos_t clipBegin,
hpatch_StreamPos_t clipEnd,const tuz_TCompressProps& props,TDictBuf& dict_buf){
std::vector<tuz_byte>& data_buf(dict_buf.dictBuf);
hpatch_StreamPos_t dictBeginPos;
const size_t dictSizeBack=data_buf.size();
{
dictBeginPos=(clipBegin<=props.dictSize)?0:(clipBegin-props.dictSize);
hpatch_StreamPos_t _mem_size=clipEnd-dictBeginPos;
checkv(_mem_size==(size_t)_mem_size);
checkv(_mem_size>=data_buf.size());
data_buf.resize((size_t)_mem_size);
}
{
hpatch_StreamPos_t readPos=dictBeginPos;
if (dict_buf.dictEndPos>readPos){
checkv(dict_buf.dictEndPos<=clipBegin);
size_t movLen=(size_t)(dict_buf.dictEndPos-readPos);
checkv(dictSizeBack>=movLen);
if (dictSizeBack-movLen>0)
memmove(data_buf.data(),data_buf.data()+dictSizeBack-movLen,movLen);
readPos=dict_buf.dictEndPos;
}
checkv(data->read(data,readPos,data_buf.data()+(size_t)(readPos-dictBeginPos),data_buf.data()+data_buf.size()));
}
TMatch matcher(data_buf.data(),data_buf.data()+data_buf.size(),coder,props);
{
const tuz_byte* end=data_buf.data()+data_buf.size();
const tuz_byte* cur=end-(clipEnd-clipBegin);
const tuz_byte* back=cur;
while (cur!=end){
const tuz_byte* matched;
size_t match_len;
if (matcher.match(&matched,&match_len,cur)){
checkv(matched<cur);
checkv(matched>=data_buf.data());
checkv(cur+match_len<=end);
checkv(match_len>=tuz_kMinDictMatchLen);
checkv(match_len<=props.maxSaveLength);
const size_t unmatched_len=(cur-back);
if (unmatched_len>0)
_outData(back,unmatched_len,coder,props);
size_t dict_pos=(cur-matched)-1;
checkv(dict_pos<props.dictSize);
coder.outDict(match_len,dict_pos);
cur+=match_len;
back=cur;
}else{
++cur;
}
}
const size_t unmatched_len=(cur-back);
if (unmatched_len>0)
_outData(back,unmatched_len,coder,props);
}
{
size_t newDictSize=(props.dictSize<=clipEnd)?props.dictSize:(size_t)clipEnd;
checkv(data_buf.size()>=newDictSize);
dict_buf.dictEndPos=clipEnd;
if (data_buf.size()>newDictSize){
memmove(data_buf.data(),data_buf.data()+(data_buf.size()-newDictSize),newDictSize);
data_buf.resize(newDictSize);
}
}
}
}
|
tinyuz\decompress\tuz_dec.c
tuz_TStream_read_dict_size Tuz 文件头解析:读取字典大小
原理与设计思路解析
tuz_TStream_read_dict_size 函数是任何 Tuz 解压操作的第一步。它的职责单一且至关重要:读取文件最开头的几个字节,并将它们转换成一个整数,这个整数代表了解压过程所需要的字典缓冲区的大小。
固定长度头部 (Fixed-Length Header)
Tuz 格式规定,压缩流的起始位置固定存储着字典的大小值。这个值占用的字节数由一个编译时常量 tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes 决定。这种设计使得头部解析非常快速和简单。
I/O 抽象 (I/O Abstraction)
为了让解压库能够适应不同的输入源(例如,从磁盘文件、内存缓冲区或网络流读取),此函数的设计并没有直接调用 fread 等具体的 I/O 函数。相反,它接受一个函数指针 read_code 作为参数。调用者必须提供一个符合 tuz_TInputStream_read 签名的函数,tuz_TStream_read_dict_size 会通过这个回调函数来完成实际的字节读取。这是一种典型的接口与实现分离的设计,增强了代码的通用性和可移植性。
小端序编码 (Little-Endian Encoding)
从文件中读取的字节数组需要被转换成一个多字节的整数。该函数遵循小端序 (Little-Endian) 的字节序约定。这意味着字节数组中的第一个字节 (saved[0]) 是整数的最低有效位字节 (Least Significant Byte, LSB),第二个字节 (saved[1]) 是次低位,以此类推。
编译时优化 (Compile-Time Optimization)
代码中使用了 #if/#elif 预处理指令,而不是运行时的 switch 或 if 语句。这是因为字典大小占用的字节数 tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes 是一个在编译时就确定的常量。通过使用预处理器,编译器只会将与该常量值匹配的代码块编译进最终的程序中,从而生成更小、更快的机器码。例如,如果 tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes 被定义为 4,那么所有其他分支(==1, ==2, ==3)的代码都不会出现在最终的可执行文件中。
代码解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
tuz_size_t tuz_TStream_read_dict_size(tuz_TInputStreamHandle inputStream,tuz_TInputStream_read read_code){
tuz_size_t v=tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes;
tuz_byte saved[tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes];
assert(read_code!=0);
if ((read_code(inputStream,saved,&v))&&(v==tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes)){
#if (tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes==1)
v=saved[0];
assert(v>0);
#elif (tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes==2)
v=saved[0]|(((tuz_size_t)saved[1])<<8);
assert((v>0)&(((v>>8)&0xFF)==saved[1]));
#elif (tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes==3)
v=saved[0]|(((tuz_size_t)saved[1])<<8)|(((tuz_size_t)saved[2])<<16);
assert((v>0)&(((v>>8)&0xFF)==saved[1])&((v>>16)==saved[2]));
#elif (tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes==4)
v=saved[0]|(((tuz_size_t)saved[1])<<8)|(((tuz_size_t)saved[2])<<16)|(((tuz_size_t)saved[3])<<24);
assert((v>0)&(((v>>8)&0xFF)==saved[1])&(((v>>16)&0xFF)==saved[2])&((v>>24)==saved[3]));
#else
# error unsupport tuz_kDictSizeSavedBytes
#endif
return v;
}else{
return 0;
}
}
|
tuz_TStream_decompress_partial Tuz 流式解压核心状态机
- 作为流式解压模型的核心,此函数负责执行实际的解压工作。它的设计精髓在于作为一个可重入 (Re-entrant) 的状态机,能够根据提供的输出缓冲区大小,解压部分或全部数据,并在暂停后能从断点处精确恢复。
原理与设计思路解析
tuz_TStream_decompress_partial 的设计核心是一个基于 goto 和状态变量的、高度优化的主循环。它模拟了一个状态机,可以在几个核心状态之间切换:“从字典复制”、“从输入流复制字面量”(可选编译)、以及**“解析新指令”**。
代码解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
|
tuz_TResult tuz_TStream_decompress_partial(tuz_TStream* self,tuz_byte* cur_out_data,tuz_size_t* data_size){
tuz_byte* const out_data_end=cur_out_data+(*data_size);
#ifdef __RUN_MEM_SAFE_CHECK
const tuz_BOOL isNeedOut=(cur_out_data<out_data_end);
#endif
for(;;){
copyDict_cmp_process:
if (self->_state.dictType_len){
if (cur_out_data<out_data_end){
const tuz_byte bdata=_dict_read_byte(self);
_dict_write_byte(self,bdata);
*cur_out_data++=bdata;
self->_state.dictType_len--;
goto copyDict_cmp_process;
}else{
break;
}
}
#if tuz_isNeedLiteralLine
copyLiteral_cmp_process:
if (self->_state.literalType_len){
if (cur_out_data<out_data_end){
const tuz_byte bdata=_cache_read_1byte(&self->_code_cache);
_dict_write_byte(self,bdata);
*cur_out_data++=bdata;
self->_state.literalType_len--;
goto copyLiteral_cmp_process;
}else{
break;
}
}
#endif
type_process:
{
if (_cache_read_1bit(self)==tuz_codeType_dict){
tuz_size_t saved_len=_cache_unpack_len(self);
tuz_size_t saved_dict_pos;
if ((self->_state.isHaveData_back)&&(_cache_read_1bit(self))){
saved_dict_pos=self->_state.dict_pos_back;
}else{
saved_dict_pos=_cache_unpack_dict_pos(self);
if (saved_dict_pos>tuz_kBigPosForLen) ++saved_len;
}
self->_state.isHaveData_back=tuz_FALSE;
if (saved_dict_pos){
self->_state.dict_pos_back=saved_dict_pos;
self->_state.dictType_len=saved_len+tuz_kMinDictMatchLen;
saved_dict_pos=(self->_dict.dict_size-saved_dict_pos);
self->_state.dictType_pos=saved_dict_pos;
continue;
}else{
#if tuz_isNeedLiteralLine
if (tuz_ctrlType_literalLine==saved_len){
self->_state.isHaveData_back=tuz_TRUE;
self->_state.literalType_len=_cache_unpack_pos_len(self)+tuz_kMinLiteralLen;
continue;
}
#endif
self->_state.dict_pos_back=1;
self->_state.type_count=0;
if (tuz_ctrlType_clipEnd==saved_len){
goto type_process;
}else if (tuz_ctrlType_streamEnd==saved_len){
(*data_size)-=(tuz_size_t)(out_data_end-cur_out_data);
return tuz_STREAM_END;
}else{
return _cache_success_finish(&self->_code_cache)?
tuz_CTRLTYPE_UNKNOW_ERROR:tuz_READ_CODE_ERROR;
}
}
}else{
if (cur_out_data<out_data_end){
const tuz_byte bdata=_cache_read_1byte(&self->_code_cache);
_dict_write_byte(self,bdata);
*cur_out_data++=bdata;
self->_state.isHaveData_back=tuz_TRUE;
goto type_process;
}else{
_cache_push_1bit(self,tuz_codeType_data);
break;
}
}
}
}
{
assert(cur_out_data==out_data_end);
if (!_cache_success_finish(&self->_code_cache))
return tuz_READ_CODE_ERROR;
#ifdef __RUN_MEM_SAFE_CHECK
return isNeedOut?tuz_OK:tuz_OUT_SIZE_OR_CODE_ERROR;
#else
return tuz_OK;
#endif
}
}
|