[TOC]
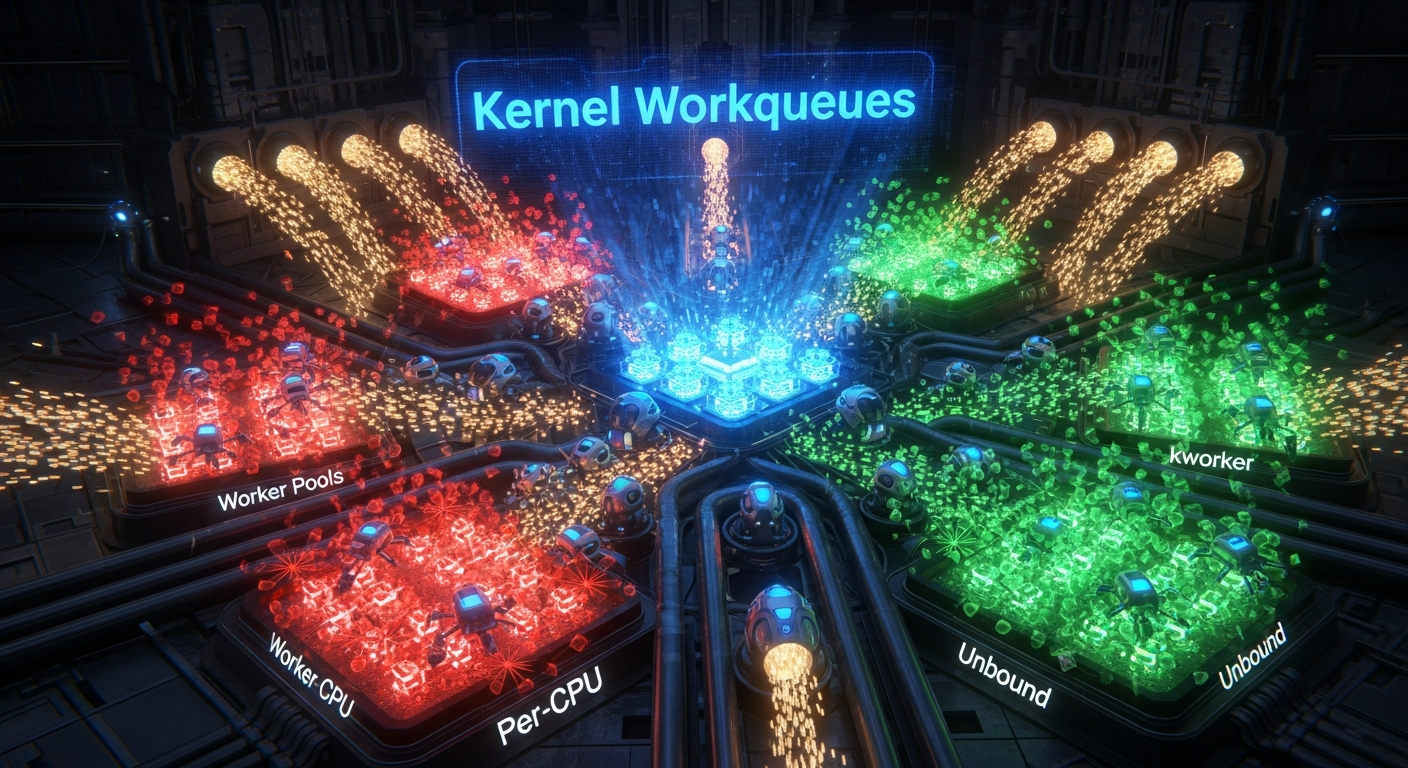
kernel/workqueue.c 内核工作队列(Kernel Workqueues) 通用的内核后台任务处理框架 历史与背景 这项技术是为了解决什么特定 “问题而诞生的? kernel/workqueue.c 实现了**工作队列(Workqueues)**机制,它的诞生是为了解决内核中一个极其普遍的需求:将一个函数的执行推迟(defer)到一个安全的进程上下文中去完成,特别是在中断处理程序中。
在内核中,代码的执行上下文非常重要,主要分为两种:
进程上下文(Process Context) :代码代表一个特定的进程(或内核线程)在运行。在这种上下文中,代码可以做任何可能导致**睡眠(blocking/sleep)**的操作,例如:获取互斥锁(mutex)、分配大块内存(kmalloc(GFP_KERNEL))、与用户空间拷贝数据、执行磁盘I/O等。中断上下文(Interrupt Context) :代码是作为对一个硬件中断的响应而运行的。中断处理程序必须尽快 完成,并且绝对不能睡眠 。如果它睡眠了,可能会导致整个系统死锁或错过其他重要的硬件中断。
这就产生了一个经典问题:一个中断处理程序(例如,网卡驱动的中断处理函数在收到一个数据包后)可能需要执行一些复杂且耗时的操作,其中某些操作还可能会睡眠。它显然不能在中断上下文中直接完成这些工作。
工作队列就是为了解决这个问题而设计的通用“下半部”(bottom-half)处理机制 。它允许中断处理程序(或其他任何不能睡眠的代码)将一个需要睡眠或耗时较长的工作任务,“排队”给一个在安全的进程上下文中运行的内核线程 去执行。
它的发展经历了哪些重要的里程碑或版本迭代? 工作队列是内核中演进最复杂的子系统之一,其核心驱动力是性能、并发性和易用性 。
早期实现 (基于keventd) :最初,内核有一个全局的事件守护进程keventd,所有模块都将工作排队给它。这非常简单,但也存在严重问题:所有工作都在一个单独的线程中串行执行,一个耗时的工作会阻塞所有其他工作;同时也无法很好地利用多核CPU的优势。引入Per-CPU工作线程 :为了提高并发性,工作队列模型演变为为每个CPU核心都创建一组工作者线程(worker threads)。这使得工作可以在多个CPU上并行执行,是一个巨大的进步。并发管理工作队列 (Concurrency-Managed Workqueues, CMWQ) :这是由Tejun Heo主导的一次革命性的重构 。CMWQ在Linux 3.x内核中被引入,它彻底改变了工作队列的实现。CMWQ的目标是动态地、按需地 管理工作者线程的数量,而不是为每个工作队列都创建固定的线程。它通过一个复杂的池化和调度算法,在提供高并发性的同时,极大地减少了系统中不必要的内核线程数量,从而降低了内存消耗和调度开销。这是当前工作队列的实现基础。
目前该技术的社区活跃度和主流应用情况如何? 工作队列是Linux内核中最基础、使用最广泛的异步执行机制 ,没有之一。
主流应用 :几乎内核的每一个子系统都在使用工作队列。
设备驱动 :绝大多数驱动的中断处理下半部。文件系统 :执行延迟写入(writeback)、日志提交等。网络 :处理一些复杂的协议栈任务。RCU :call_rcu()的回调函数通常就是通过一个工作队列来执行的。
核心原理与设计 它的核心工作原理是什么? 现代工作队列(CMWQ)的核心是一个动态的、per-CPU的工作者线程池(worker pool) 。
核心数据结构 :
struct work_structfunc)的指针和一个用于链接的数据域。struct workqueue_structworker_pool
工作流程 :
初始化工作 (INIT_WORK) :开发者在自己的数据结构中嵌入一个work_struct,并使用INIT_WORK宏将其与一个回调函数关联起来。排队工作 (queue_work) :queue_work(wq, work)。wq是要使用的workqueue_struct,work是要排队的工作。工作者池(worker pool) 。work)会被添加到该池的待处理工作链表 中。空闲的(idle)工作者线程 被唤醒。执行工作 (由工作者线程完成) :kworker/uX:Y的内核线程)开始运行。work->func)。进程上下文 中运行的,所以这个回调函数可以安全地执行任何可能睡眠的操作。
CMWQ的动态管理 :
CMWQ会持续监控每个池的负载情况。如果一个池中的工作大量堆积,而所有工作者线程都在忙碌(例如,都在睡眠等待I/O),CMWQ会自动创建新的 工作者线程加入到这个池中,以提高并发度。
反之,如果一个池中的工作者线程长时间处于空闲状态,CMWQ会自动销毁它们,以回收资源。
它的主要优势体现在哪些方面?
上下文安全 :完美地解决了在中断上下文中执行睡眠操作的问题。简单易用 :为内核开发者提供了一个极其简单的API(INIT_WORK, queue_work)来利用复杂的后台处理能力。高效与并发 :CMWQ的动态线程池管理提供了出色的性能和并发性,同时又避免了不必要的资源浪费。通用性 :是一个高度通用的框架,可被任何需要后台处理的内核子系统使用。
它存在哪些已知的劣势、局限性或在特定场景下的不适用性?
延迟 :从工作被排队到它真正开始执行,中间存在一定的调度延迟。因此,工作队列不适合用于有严格、低延迟时间要求的“硬实时”任务。-非时间确定性 :一个工作的执行可能会被其他更高优先级的进程或同一池中的其他工作所延迟,其执行时间点是不保证的。
资源消耗 :虽然CMWQ已经很高效,但内核线程本身仍然是内核中的一种资源,大量的后台工作仍然会消耗CPU时间和内存。
使用场景 在哪些具体的业务或技术场景下,它是首选解决方案? 工作队列是从原子上下文(如中断、持有自旋锁)中推迟可能睡眠或耗时较长的工作 的首选解决方案。
中断处理下半部 :一个网卡驱动的中断处理程序(上半部)在收到数据包后,可能会快速地确认中断、从硬件DMA缓冲区中取出数据,然后调用queue_work()来安排一个工作,由该工作在进程上下文中去处理复杂的协议栈逻辑。延迟的I/O操作 :一个文件系统在需要将脏数据写回磁盘时,不会在系统调用路径上同步等待I/O完成,而是创建一个工作来异步地执行写操作。驱动中的复杂状态机 :一个USB驱动在处理设备枚举或状态变更时,涉及多个步骤,其中一些可能需要睡眠。这些通常都是通过工作队列来驱动的。
是否有不推荐使用该技术的场景?为什么?
硬实时任务 :如果一个任务必须在事件发生后的几百微秒内被处理,使用工作队列是不合适的,因为其调度延迟不可预测。这种场景可能需要使用线程化中断(threaded IRQs)。极简、高性能的下半部 :如果下半部的工作非常简单,保证不会睡眠,且对延迟要求较高,那么使用开销更低的Tasklets 或Softirqs 可能会更合适。然而,由于工作队列的易用性和安全性,现在内核社区更倾向于优先使用工作队列。
对比分析 请将其 与 其他相似技术 进行详细对比。 在Linux内核中,有多种“下半部”处理机制,它们在性能、复杂性和使用限制上各不相同。
| 特性 | 工作队列 (Workqueues) | Tasklets | Softirqs (软中断) |执行上下文 | 进程上下文 | 软中断上下文 | 软中断上下文 |是否可睡眠 | 是 | 否 | 否 |并发模型 | 并发 。工作可以在不同CPU上的不同内核线程中并行执行。 | 串行 。同一个tasklet在同一时间只能在一个CPU上运行。 | 并发 。同一个软中断的处理函数可以在多个CPU上同时运行(需要处理函数自身是可重入的)。 |性能/延迟 | 较低/延迟较高 。涉及线程调度。 | 较高/延迟较低 。 | 最高/延迟最低 。是性能最高的机制。 |使用复杂度 | 简单 。API直观,无需担心睡眠问题。 | 中等 。API简单,但不能睡眠。 | 复杂 。需要静态编译时定义,且处理函数必须是高度优化的可重入代码。 |适用场景 | 通用的、需要睡眠或耗时较长的 下半部处理。 | 延迟敏感、不睡眠、相对简单的下半部。 | 性能极其敏感的核心子系统,如网络包接收和定时器处理。 |
include/linux/workqueue.h INIT_WORK 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP #else #define __INIT_WORK_KEY(_work, _func, _onstack, _key) \ do { \ __init_work((_work), _onstack); \ (_work)->data = (atomic_long_t) WORK_DATA_INIT(); \ INIT_LIST_HEAD(&(_work)->entry); \ (_work)->func = (_func); \ } while (0) #endif #define __INIT_WORK(_work, _func, _onstack) \ do { \ static __maybe_unused struct lock_class_key __key; \ \ __INIT_WORK_KEY(_work, _func, _onstack, &__key); \ } while (0) #define INIT_WORK(_work, _func) \ __INIT_WORK((_work), (_func), 0)
queue_delayed_work 延迟后对 workqueue 上的工作进行排队 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static inline bool queue_delayed_work (struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay) { return queue_delayed_work_on(WORK_CPU_UNBOUND, wq, dwork, delay); }
kernel/workqueue_internal.h 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 static inline struct worker *current_wq_worker (void ) { if (in_task() && (current->flags & PF_WQ_WORKER)) return kthread_data(current); return NULL ; }
kernel/workqueue.c init_cpu_worker_pool 初始化 CPU 工作池 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 static int init_worker_pool (struct worker_pool *pool) { raw_spin_lock_init(&pool->lock); pool->id = -1 ; pool->cpu = -1 ; pool->node = NUMA_NO_NODE; pool->flags |= POOL_DISASSOCIATED; pool->watchdog_ts = jiffies; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pool->worklist); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pool->idle_list); hash_init(pool->busy_hash); timer_setup(&pool->idle_timer, idle_worker_timeout, TIMER_DEFERRABLE); INIT_WORK(&pool->idle_cull_work, idle_cull_fn); timer_setup(&pool->mayday_timer, pool_mayday_timeout, 0 ); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pool->workers); ida_init(&pool->worker_ida); INIT_HLIST_NODE(&pool->hash_node); pool->refcnt = 1 ; pool->attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(); if (!pool->attrs) return -ENOMEM; wqattrs_clear_for_pool(pool->attrs); return 0 ; } static void __init init_cpu_worker_pool (struct worker_pool *pool, int cpu, int nice) { BUG_ON(init_worker_pool(pool)); pool->cpu = cpu; cpumask_copy(pool->attrs->cpumask, cpumask_of(cpu)); cpumask_copy(pool->attrs->__pod_cpumask, cpumask_of(cpu)); pool->attrs->nice = nice; pool->attrs->affn_strict = true ; pool->node = cpu_to_node(cpu); mutex_lock(&wq_pool_mutex); BUG_ON(worker_pool_assign_id(pool)); mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_mutex); }
init_pwq 初始化 pwq 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 static void init_pwq (struct pool_workqueue *pwq, struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct worker_pool *pool) { BUG_ON((unsigned long )pwq & ~WORK_STRUCT_PWQ_MASK); memset (pwq, 0 , sizeof (*pwq)); pwq->pool = pool; pwq->wq = wq; pwq->flush_color = -1 ; pwq->refcnt = 1 ; INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->inactive_works); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->pending_node); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->pwqs_node); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pwq->mayday_node); kthread_init_work(&pwq->release_work, pwq_release_workfn); }
__wq_cpumask_show: 显示CPU掩码的核心实现函数这个内部静态函数是所有只读 _show 函数的核心。它接收一个cpumask变量, 并将其格式化为人类可读的字符串, 然后放入用户的缓冲区。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 static ssize_t __wq_cpumask_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf, cpumask_var_t mask) { int written; mutex_lock(&wq_pool_mutex); written = scnprintf(buf, PAGE_SIZE, "%*pb\n" , cpumask_pr_args(mask)); mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_mutex); return written; }
cpumask_requested_show & DEVICE_ATTR_RO(cpumask_requested): 显示 “requested” CPU掩码这个函数和宏组合在一起, 创建了一个名为 cpumask_requested 的只读 sysfs 文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 static ssize_t cpumask_requested_show (struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf) { return __wq_cpumask_show(dev, attr, buf, wq_requested_unbound_cpumask); } static DEVICE_ATTR_RO (cpumask_requested) ;
cpumask_isolated_show & DEVICE_ATTR_RO(cpumask_isolated): 显示 “isolated” CPU掩码这个函数和宏组合在一起, 创建了一个名为 cpumask_isolated 的只读 sysfs 文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 static ssize_t cpumask_isolated_show (struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf) { return __wq_cpumask_show(dev, attr, buf, wq_isolated_cpumask); } static DEVICE_ATTR_RO (cpumask_isolated) ;
cpumask_show, cpumask_store & DEVICE_ATTR_RW(cpumask): 显示和修改当前的CPU掩码这组函数和宏创建了一个名为 cpumask 的可读写 sysfs 文件, 这是用户最常交互的文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 static ssize_t cpumask_show (struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, char *buf) { return __wq_cpumask_show(dev, attr, buf, wq_unbound_cpumask); } static ssize_t cpumask_store (struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr, const char *buf, size_t count) { cpumask_var_t cpumask; int ret; if (!zalloc_cpumask_var(&cpumask, GFP_KERNEL)) return -ENOMEM; ret = cpumask_parse(buf, cpumask); if (!ret) ret = workqueue_set_unbound_cpumask(cpumask); free_cpumask_var(cpumask); return ret ? ret : count; } static DEVICE_ATTR_RW (cpumask) ;
wq_sysfs_cpumask_attrs & ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS: 定义属性组这部分代码将前面定义的所有属性文件打包成一个组, 以便一次性注册。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 static struct attribute *wq_sysfs_cpumask_attrs [] = &dev_attr_cpumask.attr, &dev_attr_cpumask_requested.attr, &dev_attr_cpumask_isolated.attr, NULL , }; ATTRIBUTE_GROUPS(wq_sysfs_cpumask);
wq_sysfs_init & core_initcall: 注册sysfs接口这是最后的初始化函数, 它在内核启动时被调用, 用来完成 sysfs 目录和文件的创建。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 static int __init wq_sysfs_init (void ) { return subsys_virtual_register(&wq_subsys, wq_sysfs_cpumask_groups); } core_initcall(wq_sysfs_init);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static int format_worker_id (char *buf, size_t size, struct worker *worker, struct worker_pool *pool) { if (worker->rescue_wq) return scnprintf(buf, size, "kworker/R-%s" , worker->rescue_wq->name); if (pool) { if (pool->cpu >= 0 ) return scnprintf(buf, size, "kworker/%d:%d%s" , pool->cpu, worker->id, pool->attrs->nice < 0 ? "H" : "" ); else return scnprintf(buf, size, "kworker/u%d:%d" , pool->id, worker->id); } else { return scnprintf(buf, size, "kworker/dying" ); } }
worker_enter_idle 进入空闲状态 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static void worker_enter_idle (struct worker *worker) { struct worker_pool *pool = if (WARN_ON_ONCE(worker->flags & WORKER_IDLE) || WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&worker->entry) && (worker->hentry.next || worker->hentry.pprev))) return ; worker->flags |= WORKER_IDLE; pool->nr_idle++; worker->last_active = jiffies; list_add(&worker->entry, &pool->idle_list); if (too_many_workers(pool) && !timer_pending(&pool->idle_timer)) mod_timer(&pool->idle_timer, jiffies + IDLE_WORKER_TIMEOUT); WARN_ON_ONCE(pool->nr_workers == pool->nr_idle && pool->nr_running); }
set_pf_worker 设置当前线程为工作队列工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 static void set_pf_worker (bool val) { mutex_lock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); if (val) current->flags |= PF_WQ_WORKER; else current->flags &= ~PF_WQ_WORKER; mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); }
worker_leave_idle - 离开空闲状态 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static void worker_leave_idle (struct worker *worker) { struct worker_pool *pool = if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!(worker->flags & WORKER_IDLE))) return ; worker_clr_flags(worker, WORKER_IDLE); pool->nr_idle--; list_del_init(&worker->entry); }
need_more_worker 判断是否需要唤醒或创建更多的工作线程(worker)来处理工作队列中的任务 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static bool need_more_worker (struct worker_pool *pool) { return !list_empty(&pool->worklist) && !pool->nr_running; }
may_start_working 判断是否可以开始工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 static bool may_start_working (struct worker_pool *pool) { return pool->nr_idle; }
wake_up_process 唤醒特定进程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 int wake_up_process (struct task_struct *p) { return try_to_wake_up(p, TASK_NORMAL, 0 ); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(wake_up_process);
worker_thread - 工作者线程函数
worker_thread是所有工作队列的工作者内核线程(kworker)的主体函数。当一个kworker被创建时,它的入口点就被设置为这个函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 static int worker_thread (void *__worker) { struct worker *worker = struct worker_pool *pool = set_pf_worker(true ); woke_up: raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); if (unlikely(worker->flags & WORKER_DIE)) { raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); set_pf_worker(false ); worker->pool = NULL ; ida_free(&pool->worker_ida, worker->id); return 0 ; } worker_leave_idle(worker); recheck: if (!need_more_worker(pool)) goto sleep; if (unlikely(!may_start_working(pool)) && manage_workers(worker)) goto recheck; WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)); worker_clr_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP | WORKER_REBOUND); do { struct work_struct *work = list_first_entry(&pool->worklist, struct work_struct, entry); if (assign_work(work, worker, NULL )) process_scheduled_works(worker); } while (keep_working(pool)); worker_set_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP); sleep: worker_enter_idle(worker); __set_current_state(TASK_IDLE); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); schedule(); goto woke_up; }
create_worker 创建一个新的工作队列工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 static struct worker *create_worker (struct worker_pool *pool) { struct worker *worker ; int id; id = ida_alloc(&pool->worker_ida, GFP_KERNEL); if (id < 0 ) { pr_err_once("workqueue: Failed to allocate a worker ID: %pe\n" , ERR_PTR(id)); return NULL ; } worker = alloc_worker(pool->node); if (!worker) { pr_err_once("workqueue: Failed to allocate a worker\n" ); goto fail; } worker->id = id; if (!(pool->flags & POOL_BH)) { char id_buf[WORKER_ID_LEN]; format_worker_id(id_buf, sizeof (id_buf), worker, pool); worker->task = kthread_create_on_node(worker_thread, worker, pool->node, "%s" , id_buf); if (IS_ERR(worker->task)) { if (PTR_ERR(worker->task) == -EINTR) { pr_err("workqueue: Interrupted when creating a worker thread \"%s\"\n" , id_buf); } else { pr_err_once("workqueue: Failed to create a worker thread: %pe" , worker->task); } goto fail; } set_user_nice(worker->task, pool->attrs->nice); kthread_bind_mask(worker->task, pool_allowed_cpus(pool)); } worker_attach_to_pool(worker, pool); raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); worker->pool->nr_workers++; worker_enter_idle(worker); if (worker->task) wake_up_process(worker->task); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); return worker; fail: ida_free(&pool->worker_ida, id); kfree(worker); return NULL ; }
maybe_create_worker 可能创建一个新的工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 - __releases(&pool->lock) 这个标记表示函数在执行过程中会释放 pool->lock 锁。它告诉静态分析工具,在进入函数时,调用者必须已经持有 pool->lock,并且函数在某些操作中释放该锁。 - __acquires(&pool->lock) 这个标记表示函数在执行过程中会重新获取 pool->lock 锁。它告诉静态分析工具,函数在退出时会确保重新持有该锁。 - 作用 这些标记的主要作用是帮助静态分析工具(如 sparse)验证锁的使用是否正确。例如: 确保在调用 maybe_create_worker 之前,调用者已经持有 pool->lock。 确保函数在退出时重新获取了 pool->lock,以避免锁的状态不一致。 ```c static void maybe_create_worker (struct worker_pool *pool) __releases (&pool->lock) __acquires (&pool->lock) { restart: raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); mod_timer(&pool->mayday_timer, jiffies + MAYDAY_INITIAL_TIMEOUT); while (true ) { if (create_worker(pool) || !need_to_create_worker(pool)) break ; schedule_timeout_interruptible(CREATE_COOLDOWN); if (!need_to_create_worker(pool)) break ; } timer_delete_sync(&pool->mayday_timer); raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); if (need_to_create_worker(pool)) goto restart; }
manage_workers 管理工作池 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 static bool manage_workers (struct worker *worker) { struct worker_pool *pool = if (pool->flags & POOL_MANAGER_ACTIVE) return false ; pool->flags |= POOL_MANAGER_ACTIVE; pool->manager = worker; maybe_create_worker(pool); pool->manager = NULL ; pool->flags &= ~POOL_MANAGER_ACTIVE; rcuwait_wake_up(&manager_wait); return true ; }
find_worker_executing_work 查找正在执行工作项的工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 static struct worker *find_worker_executing_work (struct worker_pool *pool, struct work_struct *work) { struct worker *worker ; hash_for_each_possible(pool->busy_hash, worker, hentry, (unsigned long )work) if (worker->current_work == work && worker->current_func == work->func) return worker; return NULL ; }
move_linked_works 移动关联的工作项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 static void move_linked_works (struct work_struct *work, struct list_head *head, struct work_struct **nextp) { struct work_struct *n ; list_for_each_entry_safe_from(work, n, NULL , entry) { list_move_tail(&work->entry, head); if (!(*work_data_bits(work) & WORK_STRUCT_LINKED)) break ; } if (nextp) *nextp = n; }
assign_work 分配工作项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 static bool assign_work (struct work_struct *work, struct worker *worker, struct work_struct **nextp) { struct worker_pool *pool = struct worker *collision ; lockdep_assert_held(&pool->lock); collision = find_worker_executing_work(pool, work); if (unlikely(collision)) { move_linked_works(work, &collision->scheduled, nextp); return false ; } move_linked_works(work, &worker->scheduled, nextp); return true ; }
keep_working 判断是否需要继续工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 static bool keep_working (struct worker_pool *pool) { return !list_empty(&pool->worklist) && (pool->nr_running <= 1 ); }
get_pwq 获取指定pool_workqueue的额外引用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 static void get_pwq (struct pool_workqueue *pwq) { lockdep_assert_held(&pwq->pool->lock); WARN_ON_ONCE(pwq->refcnt <= 0 ); pwq->refcnt++; }
put_pwq 取消对 @pwq 的引用。如果它的引用计数降为零,安排销毁它。调用者应该持有匹配的 pool->lock。 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 static void put_pwq (struct pool_workqueue *pwq) { lockdep_assert_held(&pwq->pool->lock); if (likely(--pwq->refcnt)) return ; kthread_queue_work(pwq_release_worker, &pwq->release_work); }
get_work_color 从 work_data 中提取工作项的颜色(color) 1 2 3 4 5 static int get_work_color (unsigned long work_data) { return (work_data >> WORK_STRUCT_COLOR_SHIFT) & ((1 << WORK_STRUCT_COLOR_BITS) - 1 ); }
pwq_dec_nr_in_flight 减少 pwq 的 nr_in_flight 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 static void pwq_dec_nr_in_flight (struct pool_workqueue *pwq, unsigned long work_data) { int color = get_work_color(work_data); if (!(work_data & WORK_STRUCT_INACTIVE)) pwq_dec_nr_active(pwq); pwq->nr_in_flight[color]--; if (likely(pwq->flush_color != color)) goto out_put; if (pwq->nr_in_flight[color]) goto out_put; pwq->flush_color = -1 ; if (atomic_dec_and_test(&pwq->wq->nr_pwqs_to_flush)) complete(&pwq->wq->first_flusher->done); out_put: put_pwq(pwq); }
first_idle_worker 返回第一个空闲的 worker 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 static struct worker *first_idle_worker (struct worker_pool *pool) { if (unlikely(list_empty(&pool->idle_list))) return NULL ; return list_first_entry(&pool->idle_list, struct worker, entry); }
need_more_worker 判断工作池(worker_pool)是否需要唤醒更多的工作线程(worker) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 static bool need_more_worker (struct worker_pool *pool) { return !list_empty(&pool->worklist) && !pool->nr_running; }
kick_bh_pool 用于唤醒软中断(Bottom Half,简称 BH)工作池中的工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 static void kick_bh_pool (struct worker_pool *pool) { if (pool->attrs->nice == HIGHPRI_NICE_LEVEL) raise_softirq_irqoff(HI_SOFTIRQ); else raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ); }
kick_pool 如有必要,唤醒空闲的 worker 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 static bool kick_pool (struct worker_pool *pool) { struct worker *worker = struct task_struct *p ; lockdep_assert_held(&pool->lock); if (!need_more_worker(pool) || !worker) return false ; if (pool->flags & POOL_BH) { kick_bh_pool(pool); return true ; } p = worker->task; wake_up_process(p); return true ; }
process_one_work 处理单个工作项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 static void process_one_work (struct worker *worker, struct work_struct *work) __releases (&pool->lock) __acquires (&pool->lock) { struct pool_workqueue *pwq = struct worker_pool *pool = unsigned long work_data; int lockdep_start_depth, rcu_start_depth; bool bh_draining = pool->flags & POOL_BH_DRAINING; WARN_ON_ONCE(!(pool->flags & POOL_DISASSOCIATED) && raw_smp_processor_id() != pool->cpu); debug_work_deactivate(work); hash_add(pool->busy_hash, &worker->hentry, (unsigned long )work); worker->current_work = work; worker->current_func = work->func; worker->current_pwq = pwq; if (worker->task) worker->current_at = worker->task->se.sum_exec_runtime; work_data = *work_data_bits(work); worker->current_color = get_work_color(work_data); strscpy(worker->desc, pwq->wq->name, WORKER_DESC_LEN); list_del_init(&work->entry); if (unlikely(pwq->wq->flags & WQ_CPU_INTENSIVE)) worker_set_flags(worker, WORKER_CPU_INTENSIVE); kick_pool(pool); set_work_pool_and_clear_pending(work, pool->id, pool_offq_flags(pool)); pwq->stats[PWQ_STAT_STARTED]++; raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); worker->current_func(work); pwq->stats[PWQ_STAT_COMPLETED]++; raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); worker_clr_flags(worker, WORKER_CPU_INTENSIVE); worker->last_func = worker->current_func; hash_del(&worker->hentry); worker->current_work = NULL ; worker->current_func = NULL ; worker->current_pwq = NULL ; worker->current_color = INT_MAX; pwq_dec_nr_in_flight(pwq, work_data); }
process_scheduled_works 处理调度的工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 static void process_scheduled_works (struct worker *worker) { struct work_struct *work ; bool first = true ; while ((work = list_first_entry_or_null(&worker->scheduled, struct work_struct, entry))) { if (first) { worker->pool->watchdog_ts = jiffies; first = false ; } process_one_work(worker, work); } }
set_pf_worker 标识一个任务是否为工作队列(workqueue)的工作者线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 static void set_pf_worker (bool val) { mutex_lock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); if (val) current->flags |= PF_WQ_WORKER; else current->flags &= ~PF_WQ_WORKER; mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); }
worker_thread 工作线程函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 static int worker_thread (void *__worker) { struct worker *worker = struct worker_pool *pool = set_pf_worker(true ); woke_up: raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); if (unlikely(worker->flags & WORKER_DIE)) { raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); set_pf_worker(false ); worker->pool = NULL ; ida_free(&pool->worker_ida, worker->id); return 0 ; } worker_leave_idle(worker); recheck: if (!need_more_worker(pool)) goto sleep; if (unlikely(!may_start_working(pool)) && manage_workers(worker)) goto recheck; WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)); worker_clr_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP | WORKER_REBOUND); do { struct work_struct *work = list_first_entry(&pool->worklist, struct work_struct, entry); if (assign_work(work, worker, NULL )) process_scheduled_works(worker); } while (keep_working(pool)); worker_set_flags(worker, WORKER_PREP); sleep: worker_enter_idle(worker); __set_current_state(TASK_IDLE); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); schedule(); goto woke_up; }
wqattrs_hash 计算工作队列属性的哈希值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 static u32 wqattrs_hash (const struct workqueue_attrs *attrs) { u32 hash = 0 ; hash = jhash_1word(attrs->nice, hash); hash = jhash_1word(attrs->affn_strict, hash); hash = jhash(cpumask_bits(attrs->__pod_cpumask), BITS_TO_LONGS(nr_cpumask_bits) * sizeof (long ), hash); if (!attrs->affn_strict) hash = jhash(cpumask_bits(attrs->cpumask), BITS_TO_LONGS(nr_cpumask_bits) * sizeof (long ), hash); return hash; }
set_worker_dying 设置工作线程为死亡状态 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 static void set_worker_dying (struct worker *worker, struct list_head *list ) { struct worker_pool *pool = lockdep_assert_held(&pool->lock); lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); if (WARN_ON(worker->current_work) || WARN_ON(!list_empty(&worker->scheduled)) || WARN_ON(!(worker->flags & WORKER_IDLE))) return ; pool->nr_workers--; pool->nr_idle--; worker->flags |= WORKER_DIE; list_move(&worker->entry, list ); get_task_struct(worker->task); }
detach_worker 分离工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 static void unbind_worker (struct worker *worker) { lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); kthread_set_per_cpu(worker->task, -1 ); if (cpumask_intersects(wq_unbound_cpumask, cpu_active_mask)) WARN_ON_ONCE(set_cpus_allowed_ptr(worker->task, wq_unbound_cpumask) < 0 ); else WARN_ON_ONCE(set_cpus_allowed_ptr(worker->task, cpu_possible_mask) < 0 ); } static void detach_worker (struct worker *worker) { lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); unbind_worker(worker); list_del(&worker->node); }
detach_dying_workers 分离死亡的工作线程 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 static void detach_dying_workers (struct list_head *cull_list) { struct worker *worker ; list_for_each_entry(worker, cull_list, entry) detach_worker(worker); }
work_grab_pending 从 WorkList 中窃取工作项并禁用 IRQ 在 Linux 内核的 workqueue.c 文件中,offqd 是一个缩写,表示 off-queue data ,它是与 work_struct 相关的一个状态信息,用于描述工作项(work item)在从队列中移除后的状态。
具体来说,offqd 是一个结构体 work_offq_data 的实例,该结构体定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 struct work_offq_data { u32 pool_id; u32 disable; u32 flags; };
offqd 的作用offqd 的主要作用是存储工作项在从队列中移除后的一些元数据,包括:
pool_idworker_pool 的 ID,用于标识工作项之前在哪个工作池中。disableflags
offqd 的使用场景offqd 主要在以下场景中使用:
工作项从队列中移除时 :off-queue 状态,此时会使用 offqd 来存储相关的元数据。
工作项禁用和启用 :offqd 的 disable 字段用于记录工作项的禁用状态。通过 disable_work() 和 enable_work() 函数,可以增加或减少禁用计数,从而控制工作项是否可以被重新排队。
工作项状态标志的管理 :offqd 的 flags 字段用于存储工作项的额外状态信息,例如是否是 BH 类型的工作项(通过 WORK_OFFQ_BH 标志表示)。
总结 offqd 是 workqueue 子系统中用于管理工作项状态的一个辅助数据结构,主要用于记录工作项在从队列中移除后的元数据,包括所属的工作池 ID、禁用计数和状态标志。它在工作项的禁用、启用以及状态转换过程中起到了重要作用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 static int try_to_grab_pending (struct work_struct *work, u32 cflags, unsigned long *irq_flags) { struct worker_pool *pool ; struct pool_workqueue *pwq ; local_irq_save(*irq_flags); if (cflags & WORK_CANCEL_DELAYED) { struct delayed_work *dwork = if (likely(timer_delete(&dwork->timer))) return 1 ; } if (!test_and_set_bit(WORK_STRUCT_PENDING_BIT, work_data_bits(work))) return 0 ; rcu_read_lock(); pool = get_work_pool(work); if (!pool) goto fail; raw_spin_lock(&pool->lock); pwq = get_work_pwq(work); if (pwq && pwq->pool == pool) { unsigned long work_data = *work_data_bits(work); debug_work_deactivate(work); if (work_data & WORK_STRUCT_INACTIVE) move_linked_works(work, &pwq->pool->worklist, NULL ); list_del_init(&work->entry); set_work_pool_and_keep_pending(work, pool->id, pool_offq_flags(pool)); pwq_dec_nr_in_flight(pwq, work_data); raw_spin_unlock(&pool->lock); rcu_read_unlock(); return 1 ; } raw_spin_unlock(&pool->lock); fail: rcu_read_unlock(); local_irq_restore(*irq_flags); return -EAGAIN; } static bool work_grab_pending (struct work_struct *work, u32 cflags, unsigned long *irq_flags) { int ret; while (true ) { ret = try_to_grab_pending(work, cflags, irq_flags); if (ret >= 0 ) return ret; cpu_relax(); } } static void work_offqd_unpack (struct work_offq_data *offqd, unsigned long data) { WARN_ON_ONCE(data & WORK_STRUCT_PWQ); offqd->pool_id = shift_and_mask(data, WORK_OFFQ_POOL_SHIFT, WORK_OFFQ_POOL_BITS); offqd->disable = shift_and_mask(data, WORK_OFFQ_DISABLE_SHIFT, WORK_OFFQ_DISABLE_BITS); offqd->flags = data & WORK_OFFQ_FLAG_MASK; } static void work_offqd_disable (struct work_offq_data *offqd) { const unsigned long max = (1lu << WORK_OFFQ_DISABLE_BITS) - 1 ; if (likely(offqd->disable < max)) offqd->disable++; else WARN_ONCE(true , "workqueue: work disable count overflowed\n" ); }
flush_work: 等待一个工作项完成其最后的执行 此函数是一个同步辅助函数. 它的作用是阻塞 当前的执行流程, 直到指定的工作项(work)执行完毕. 当此函数返回时, 可以保证该工作项处于空闲状态 (除非在flush_work开始执行后, 有其他代码又重新将其加入了队列). 这在设备驱动中非常关键, 例如, 在卸载一个驱动模块或关闭一个设备之前, 必须确保所有由该驱动提交的后台任务(work items)都已处理完毕, flush_work就是用来实现这种同步等待的.
在STM32H750单核系统上, 虽然不存在多核并行执行, 但并发性依然存在. 一个work是由后台的kworker内核线程执行的, 而调用flush_work的可能是另一个内核线程或进程上下文. 调用flush_work会使当前任务进入睡眠状态, 内核调度器会切换到其他任务, 比如kworker线程, 让其有机会完成待处理的工作. 因此, 即使在单核上, 这个函数对于保证操作的正确顺序也是必不可少的.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 bool flush_work (struct work_struct *work) { might_sleep(); return __flush_work(work, false ); } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(flush_work);
insert_wq_barrier: 向工作队列中插入一个屏障工作项 此函数是工作项冲刷(flush)机制的核心实现, 它的作用是原子性地将一个作为同步点的”屏障”工作项 (barr) 插入到一个工作队列中, 紧跟在需要被等待的”目标”工作项 (target) 之后. 该函数通过两种不同的策略来实现这一目标, 具体取决于目标工作项是正在执行还是仍在队列中等待.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 static void wq_barrier_func (struct work_struct *work) { struct wq_barrier *barr =struct wq_barrier, work); complete(&barr->done); } static void insert_wq_barrier (struct pool_workqueue *pwq, struct wq_barrier *barr, struct work_struct *target, struct worker *worker) { static __maybe_unused struct lock_class_key bh_key , thr_key ; unsigned int work_flags = 0 ; unsigned int work_color; struct list_head *head ; INIT_WORK_ONSTACK_KEY(&barr->work, wq_barrier_func, (pwq->wq->flags & WQ_BH) ? &bh_key : &thr_key); __set_bit(WORK_STRUCT_PENDING_BIT, work_data_bits(&barr->work)); init_completion_map(&barr->done, &target->lockdep_map); barr->task = current; work_flags |= WORK_STRUCT_INACTIVE; if (worker) { head = worker->scheduled.next; work_color = worker->current_color; } else { unsigned long *bits = work_data_bits(target); head = target->entry.next; work_flags |= *bits & WORK_STRUCT_LINKED; work_color = get_work_color(*bits); __set_bit(WORK_STRUCT_LINKED_BIT, bits); } pwq->nr_in_flight[work_color]++; work_flags |= work_color_to_flags(work_color); insert_work(pwq, &barr->work, head, work_flags); }
start_flush_work: 启动一个工作项的冲刷操作 此函数是 __flush_work 的核心辅助函数, 它的主要职责是在一个原子性的上下文中, 检查一个给定的工作项 (work) 是否正处于活动状态 (即, 排队中或正在执行). 如果工作项是活动的, 此函数会将一个特殊的”屏障”工作项 (barr) 插入到与目标工作项相同的执行队列中, 并返回 true, 表示调用者需要等待. 如果目标工作项已经是空闲的, 则此函数直接返回 false, 表示无需等待.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 static bool start_flush_work (struct work_struct *work, struct wq_barrier *barr, bool from_cancel) { struct worker *worker =NULL ; struct worker_pool *pool ; struct pool_workqueue *pwq ; struct workqueue_struct *wq ; rcu_read_lock(); pool = get_work_pool(work); if (!pool) { rcu_read_unlock(); return false ; } raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); pwq = get_work_pwq(work); if (pwq) { if (unlikely(pwq->pool != pool)) goto already_gone; } else { worker = find_worker_executing_work(pool, work); if (!worker) goto already_gone; pwq = worker->current_pwq; } wq = pwq->wq; check_flush_dependency(wq, work, from_cancel); insert_wq_barrier(pwq, barr, work, worker); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); touch_work_lockdep_map(work, wq); if (!from_cancel && (wq->saved_max_active == 1 || wq->rescuer)) touch_wq_lockdep_map(wq); rcu_read_unlock(); return true ; already_gone: raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); rcu_read_unlock(); return false ; }
__flush_work: 冲刷(flush)一个工作项的核心实现 这是flush_work和cancel_work_sync等函数的内部核心实现. 它的基本原理是在目标工作项work所在的CPU的工作队列上, 插入一个特殊的”屏障”(barrier)工作项. 因为同一个工作队列中的工作项是按顺序执行的, 所以当这个屏障工作项开始执行时, 就意味着它前面的所有工作项(包括我们关心的work)都已经完成了. 然后, 调用者只需等待这个屏障工作项完成即可.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 static bool __flush_work(struct work_struct *work, bool from_cancel){ struct wq_barrier barr ; if (WARN_ON(!wq_online)) return false ; if (WARN_ON(!work->func)) return false ; if (!start_flush_work(work, &barr, from_cancel)) return false ; if (from_cancel) { unsigned long data = *work_data_bits(work); if (!WARN_ON_ONCE(data & WORK_STRUCT_PWQ) && (data & WORK_OFFQ_BH)) { while (!try_wait_for_completion(&barr.done)) { if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_PREEMPT_RT)) { local_bh_disable(); local_bh_enable(); } else { cpu_relax(); } } goto out_destroy; } } wait_for_completion(&barr.done); out_destroy: destroy_work_on_stack(&barr.work); return true ; }
cancel_work 取消工作项 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 static bool __cancel_work(struct work_struct *work, u32 cflags){ struct work_offq_data offqd ; unsigned long irq_flags; int ret; ret = work_grab_pending(work, cflags, &irq_flags); work_offqd_unpack(&offqd, *work_data_bits(work)); if (cflags & WORK_CANCEL_DISABLE) work_offqd_disable(&offqd); set_work_pool_and_clear_pending(work, offqd.pool_id, work_offqd_pack_flags(&offqd)); local_irq_restore(irq_flags); return ret; } static bool __cancel_work_sync(struct work_struct *work, u32 cflags){ bool ret; ret = __cancel_work(work, cflags | WORK_CANCEL_DISABLE); if (*work_data_bits(work) & WORK_OFFQ_BH) WARN_ON_ONCE(in_hardirq()); else might_sleep(); if (wq_online) __flush_work(work, true ); if (!(cflags & WORK_CANCEL_DISABLE)) enable_work(work); return ret; } bool cancel_work (struct work_struct *work) { return __cancel_work(work, 0 ); } EXPORT_SYMBOL(cancel_work);
put_unbound_pool 释放工作池 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 static void put_unbound_pool (struct worker_pool *pool) { struct worker *worker ; LIST_HEAD(cull_list); lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_mutex); if (--pool->refcnt) return ; if (WARN_ON(!(pool->cpu < 0 )) || WARN_ON(!list_empty(&pool->worklist))) return ; if (pool->id >= 0 ) idr_remove(&worker_pool_idr, pool->id); hash_del(&pool->hash_node); while (true ) { rcuwait_wait_event(&manager_wait, !(pool->flags & POOL_MANAGER_ACTIVE), TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE); mutex_lock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); if (!(pool->flags & POOL_MANAGER_ACTIVE)) { pool->flags |= POOL_MANAGER_ACTIVE; break ; } raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); } while ((worker = first_idle_worker(pool))) set_worker_dying(worker, &cull_list); WARN_ON(pool->nr_workers || pool->nr_idle); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); detach_dying_workers(&cull_list); mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_attach_mutex); reap_dying_workers(&cull_list); timer_delete_sync(&pool->idle_timer); cancel_work_sync(&pool->idle_cull_work); timer_delete_sync(&pool->mayday_timer); call_rcu(&pool->rcu, rcu_free_pool); }
get_unbound_pool 获取具有指定属性的工作池 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 static DEFINE_HASHTABLE (unbound_pool_hash, UNBOUND_POOL_HASH_ORDER) ;static struct worker_pool *get_unbound_pool (const struct workqueue_attrs *attrs) { struct wq_pod_type *pt = u32 hash = wqattrs_hash(attrs); struct worker_pool *pool ; int pod, node = NUMA_NO_NODE; lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_mutex); hash_for_each_possible(unbound_pool_hash, pool, hash_node, hash) { if (wqattrs_equal(pool->attrs, attrs)) { pool->refcnt++; return pool; } } for (pod = 0 ; pod < pt->nr_pods; pod++) { if (cpumask_subset(attrs->__pod_cpumask, pt->pod_cpus[pod])) { node = pt->pod_node[pod]; break ; } } pool = kzalloc_node(sizeof (*pool), GFP_KERNEL, node); if (!pool || init_worker_pool(pool) < 0 ) goto fail; pool->node = node; copy_workqueue_attrs(pool->attrs, attrs); wqattrs_clear_for_pool(pool->attrs); if (worker_pool_assign_id(pool) < 0 ) goto fail; if (wq_online && !create_worker(pool)) goto fail; hash_add(unbound_pool_hash, &pool->hash_node, hash); return pool; fail: if (pool) put_unbound_pool(pool); return NULL ; }
alloc_unbound_pwq 用于根据给定的属性 attrs 获取一个合适的 worker pool 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 static struct pool_workqueue *alloc_unbound_pwq (struct workqueue_struct *wq, const struct workqueue_attrs *attrs) { struct worker_pool *pool ; struct pool_workqueue *pwq ; lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_mutex); pool = get_unbound_pool(attrs); if (!pool) return NULL ; pwq = kmem_cache_alloc_node(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL, pool->node); if (!pwq) { put_unbound_pool(pool); return NULL ; } init_pwq(pwq, wq, pool); return pwq; }
apply_wqattrs_prepare 应用工作队列属性 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 static struct apply_wqattrs_ctx *apply_wqattrs_prepare (struct workqueue_struct *wq, const struct workqueue_attrs *attrs, const cpumask_var_t unbound_cpumask) { struct apply_wqattrs_ctx *ctx ; struct workqueue_attrs *new_attrs ; int cpu; lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_mutex); if (WARN_ON(attrs->affn_scope < 0 || attrs->affn_scope >= WQ_AFFN_NR_TYPES)) return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL); ctx = kzalloc(struct_size(ctx, pwq_tbl, nr_cpu_ids), GFP_KERNEL); new_attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(); if (!ctx || !new_attrs) goto out_free; copy_workqueue_attrs(new_attrs, attrs); wqattrs_actualize_cpumask(new_attrs, unbound_cpumask); cpumask_copy(new_attrs->__pod_cpumask, new_attrs->cpumask); ctx->dfl_pwq = alloc_unbound_pwq(wq, new_attrs); if (!ctx->dfl_pwq) goto out_free; for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { if (new_attrs->ordered) { ctx->dfl_pwq->refcnt++; ctx->pwq_tbl[cpu] = ctx->dfl_pwq; } else { wq_calc_pod_cpumask(new_attrs, cpu); ctx->pwq_tbl[cpu] = alloc_unbound_pwq(wq, new_attrs); if (!ctx->pwq_tbl[cpu]) goto out_free; } } copy_workqueue_attrs(new_attrs, attrs); cpumask_and(new_attrs->cpumask, new_attrs->cpumask, cpu_possible_mask); cpumask_copy(new_attrs->__pod_cpumask, new_attrs->cpumask); ctx->attrs = new_attrs; if ((wq->flags & __WQ_ORDERED) && !list_empty(&wq->pwqs)) ctx->dfl_pwq->plugged = true ; ctx->wq = wq; return ctx; out_free: free_workqueue_attrs(new_attrs); apply_wqattrs_cleanup(ctx); return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM); }
apply_wqattrs_commit 应用新的工作队列属性(wqattrs),并将准备好的 pwqs(per-CPU workqueues)安装到工作队列中 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 static void apply_wqattrs_commit (struct apply_wqattrs_ctx *ctx) { int cpu; mutex_lock(&ctx->wq->mutex); copy_workqueue_attrs(ctx->wq->unbound_attrs, ctx->attrs); for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) ctx->pwq_tbl[cpu] = install_unbound_pwq(ctx->wq, cpu, ctx->pwq_tbl[cpu]); ctx->dfl_pwq = install_unbound_pwq(ctx->wq, -1 , ctx->dfl_pwq); wq_update_node_max_active(ctx->wq, -1 ); if (ctx->wq->rescuer) set_cpus_allowed_ptr(ctx->wq->rescuer->task, unbound_effective_cpumask(ctx->wq)); mutex_unlock(&ctx->wq->mutex); }
apply_workqueue_attrs_locked 在加锁状态下为 workqueue(工作队列)应用新的属性 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 static int apply_workqueue_attrs_locked (struct workqueue_struct *wq, const struct workqueue_attrs *attrs) { struct apply_wqattrs_ctx *ctx ; if (WARN_ON(!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND))) return -EINVAL; ctx = apply_wqattrs_prepare(wq, attrs, wq_unbound_cpumask); if (IS_ERR(ctx)) return PTR_ERR(ctx); apply_wqattrs_commit(ctx); apply_wqattrs_cleanup(ctx); return 0 ; }
alloc_and_link_pwqs 分配并链接工作队列池(PWQ) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 static int alloc_and_link_pwqs (struct workqueue_struct *wq) { bool highpri = wq->flags & WQ_HIGHPRI; int cpu, ret; lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_mutex); wq->cpu_pwq = alloc_percpu(struct pool_workqueue *); if (!wq->cpu_pwq) goto enomem; if (!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND)) { struct worker_pool __percpu *pools ; if (wq->flags & WQ_BH) pools = bh_worker_pools; else pools = cpu_worker_pools; for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { struct pool_workqueue **pwq_p ; struct worker_pool *pool ; pool = &(per_cpu_ptr(pools, cpu)[highpri]); pwq_p = per_cpu_ptr(wq->cpu_pwq, cpu); *pwq_p = kmem_cache_alloc_node(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL, pool->node); if (!*pwq_p) goto enomem; init_pwq(*pwq_p, wq, pool); mutex_lock(&wq->mutex); link_pwq(*pwq_p); mutex_unlock(&wq->mutex); } return 0 ; } if (wq->flags & __WQ_ORDERED) { struct pool_workqueue *dfl_pwq ; ret = apply_workqueue_attrs_locked(wq, ordered_wq_attrs[highpri]); dfl_pwq = rcu_access_pointer(wq->dfl_pwq); WARN(!ret && (wq->pwqs.next != &dfl_pwq->pwqs_node || wq->pwqs.prev != &dfl_pwq->pwqs_node), "ordering guarantee broken for workqueue %s\n" , wq->name); } else { ret = apply_workqueue_attrs_locked(wq, unbound_std_wq_attrs[highpri]); } return ret; enomem: if (wq->cpu_pwq) { for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { struct pool_workqueue *pwq = if (pwq) kmem_cache_free(pwq_cache, pwq); } free_percpu(wq->cpu_pwq); wq->cpu_pwq = NULL ; } return -ENOMEM; }
alloc_workqueue 分配工作队列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 __printf(1 , 0 ) static struct workqueue_struct *__alloc_workqueue (const char *fmt , unsigned int flags , int max_active , va_list args ) { struct workqueue_struct *wq ; size_t wq_size; int name_len; if (flags & WQ_BH) { if (WARN_ON_ONCE(flags & ~__WQ_BH_ALLOWS)) return NULL ; if (WARN_ON_ONCE(max_active)) return NULL ; } if ((flags & WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT) && wq_power_efficient) flags |= WQ_UNBOUND; if (flags & WQ_UNBOUND) wq_size = struct_size(wq, node_nr_active, nr_node_ids + 1 ); else wq_size = sizeof (*wq); wq = kzalloc(wq_size, GFP_KERNEL); if (!wq) return NULL ; if (flags & WQ_UNBOUND) { wq->unbound_attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs(); if (!wq->unbound_attrs) goto err_free_wq; } name_len = vsnprintf(wq->name, sizeof (wq->name), fmt, args); if (name_len >= WQ_NAME_LEN) pr_warn_once("workqueue: name exceeds WQ_NAME_LEN. Truncating to: %s\n" , wq->name); if (flags & WQ_BH) { max_active = INT_MAX; } else { max_active = max_active ?: WQ_DFL_ACTIVE; max_active = wq_clamp_max_active(max_active, flags, wq->name); } wq->flags = flags; wq->max_active = max_active; wq->min_active = min(max_active, WQ_DFL_MIN_ACTIVE); wq->saved_max_active = wq->max_active; wq->saved_min_active = wq->min_active; mutex_init(&wq->mutex); atomic_set (&wq->nr_pwqs_to_flush, 0 ); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wq->pwqs); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wq->flusher_queue); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wq->flusher_overflow); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wq->maydays); INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wq->list ); if (flags & WQ_UNBOUND) { if (alloc_node_nr_active(wq->node_nr_active) < 0 ) goto err_free_wq; } apply_wqattrs_lock(); if (alloc_and_link_pwqs(wq) < 0 ) goto err_unlock_free_node_nr_active; mutex_lock(&wq->mutex); wq_adjust_max_active(wq); mutex_unlock(&wq->mutex); list_add_tail_rcu(&wq->list , &workqueues); if (wq_online && init_rescuer(wq) < 0 ) goto err_unlock_destroy; apply_wqattrs_unlock(); if ((wq->flags & WQ_SYSFS) && workqueue_sysfs_register(wq)) goto err_destroy; return wq; err_unlock_free_node_nr_active: apply_wqattrs_unlock(); if (wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND) { kthread_flush_worker(pwq_release_worker); free_node_nr_active(wq->node_nr_active); } err_free_wq: free_workqueue_attrs(wq->unbound_attrs); kfree(wq); return NULL ; err_unlock_destroy: apply_wqattrs_unlock(); err_destroy: destroy_workqueue(wq); return NULL ; } __printf(1 , 4 ) struct workqueue_struct *alloc_workqueue (const char *fmt, unsigned int flags, int max_active, ...) { struct workqueue_struct *wq ; va_list args; va_start(args, max_active); wq = __alloc_workqueue(fmt, flags, max_active, args); va_end(args); if (!wq) return NULL ; wq_init_lockdep(wq); return wq; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(alloc_workqueue);
workqueue_init_early 工作队初始化 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 #define for_each_bh_worker_pool(pool, cpu) \ for ((pool) = &per_cpu(bh_worker_pools, cpu)[0]; \ (pool) < &per_cpu(bh_worker_pools, cpu)[NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS]; \ (pool)++) #define for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) \ for ((pool) = &per_cpu(cpu_worker_pools, cpu)[0]; \ (pool) < &per_cpu(cpu_worker_pools, cpu)[NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS]; \ (pool)++) void __init workqueue_init_early (void ) { struct wq_pod_type *pt = int std_nice[NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS] = { 0 , HIGHPRI_NICE_LEVEL }; void (*irq_work_fns[2 ])(struct irq_work *) = { bh_pool_kick_normal, bh_pool_kick_highpri }; int i, cpu; pwq_cache = KMEM_CACHE(pool_workqueue, SLAB_PANIC); unbound_wq_update_pwq_attrs_buf = alloc_workqueue_attrs(); BUG_ON(!unbound_wq_update_pwq_attrs_buf); pt->pod_cpus = kcalloc(1 , sizeof (pt->pod_cpus[0 ]), GFP_KERNEL); pt->pod_node = kcalloc(1 , sizeof (pt->pod_node[0 ]), GFP_KERNEL); pt->cpu_pod = kcalloc(nr_cpu_ids, sizeof (pt->cpu_pod[0 ]), GFP_KERNEL); BUG_ON(!pt->pod_cpus || !pt->pod_node || !pt->cpu_pod); pt->nr_pods = 1 ; cpumask_copy(pt->pod_cpus[0 ], cpu_possible_mask); pt->pod_node[0 ] = NUMA_NO_NODE; pt->cpu_pod[0 ] = 0 ; for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { struct worker_pool *pool ; i = 0 ; for_each_bh_worker_pool(pool, cpu) { init_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu, std_nice[i]); pool->flags |= POOL_BH; init_irq_work(bh_pool_irq_work(pool), irq_work_fns[i]); i++; } i = 0 ; for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) init_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu, std_nice[i++]); } for (i = 0 ; i < NR_STD_WORKER_POOLS; i++) { struct workqueue_attrs *attrs ; BUG_ON(!(attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs())); attrs->nice = std_nice[i]; unbound_std_wq_attrs[i] = attrs; BUG_ON(!(attrs = alloc_workqueue_attrs())); attrs->nice = std_nice[i]; attrs->ordered = true ; ordered_wq_attrs[i] = attrs; } system_wq = alloc_workqueue("events" , 0 , 0 ); system_highpri_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_highpri" , WQ_HIGHPRI, 0 ); system_long_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_long" , 0 , 0 ); system_unbound_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_unbound" , WQ_UNBOUND, WQ_MAX_ACTIVE); system_freezable_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_freezable" , WQ_FREEZABLE, 0 ); system_power_efficient_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_power_efficient" , WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT, 0 ); system_freezable_power_efficient_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_freezable_pwr_efficient" , WQ_FREEZABLE | WQ_POWER_EFFICIENT, 0 ); system_bh_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_bh" , WQ_BH, 0 ); system_bh_highpri_wq = alloc_workqueue("events_bh_highpri" , WQ_BH | WQ_HIGHPRI, 0 ); BUG_ON(!system_wq || !system_highpri_wq || !system_long_wq || !system_unbound_wq || !system_freezable_wq || !system_power_efficient_wq || !system_freezable_power_efficient_wq || !system_bh_wq || !system_bh_highpri_wq); }
for_each_pool 遍历工作池 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 #define for_each_pool(pool, pi) \ idr_for_each_entry(&worker_pool_idr, pool, pi) \ if (({ assert_rcu_or_pool_mutex(); false; })) { } \ else
is_chained_work 判断当前工作项是否是由同一工作队列执行的另一个工作项触发 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 static bool is_chained_work (struct workqueue_struct *wq) { struct worker *worker ; worker = current_wq_worker(); return worker && worker->current_pwq->wq == wq; }
work_struct_pwq 将工作项的 data 字段转换为 pool_workqueue
该函数用于从工作项的 data 字段中提取与之关联的工作池(pool_workqueue)。
该函数假设 data 字段包含了一个指向 pool_workqueue 的指针,并且使用 WORK_STRUCT_PWQ_MASK 进行掩码操作。
注意:此函数仅在工作项确实与一个 pool_workqueue 相关联时才有效。
1 2 3 4 static inline struct pool_workqueue *work_struct_pwq (unsigned long data) { return (struct pool_workqueue *)(data & WORK_STRUCT_PWQ_MASK); }
get_work_pool 返回与给定作品关联的worker_pool 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 static struct worker_pool *get_work_pool (struct work_struct *work) { unsigned long data = atomic_long_read(&work->data); int pool_id; assert_rcu_or_pool_mutex(); if (data & WORK_STRUCT_PWQ) return work_struct_pwq(data)->pool; pool_id = data >> WORK_OFFQ_POOL_SHIFT; if (pool_id == WORK_OFFQ_POOL_NONE) return NULL ; return idr_find(&worker_pool_idr, pool_id); }
find_worker_executing_work 查找正在执行工作的 worker 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 static struct worker *find_worker_executing_work (struct worker_pool *pool, struct work_struct *work) { struct worker *worker ; hash_for_each_possible(pool->busy_hash, worker, hentry, (unsigned long )work) if (worker->current_work == work && worker->current_func == work->func) return worker; return NULL ; }
set_work_data 设置工作项的 data 字段
队列状态:
当工作项被排队时,WORK_STRUCT_PWQ 标志位被设置,表示工作项已关联到一个工作队列(pwq)。
此时,data 的非标志位部分存储指向队列的指针(pwq)。
一旦工作项开始执行,WORK_STRUCT_PWQ 标志位被清除,data 的高位部分存储脱队(OFFQ)标志和工作池 ID。
状态设置函数:
set_work_pwq()、set_work_pool_and_clear_pending() 和 mark_work_canceling() 是用于设置工作项状态的函数。这些函数可以设置工作队列(pwq)、工作池(pool)或清除 work->data。
这些函数只能在工作项被“拥有”(即 PENDING 位被设置)时调用,确保工作项的状态不会被其他线程竞争修改。
状态获取函数:
get_work_pool() 和 get_work_pwq() 用于获取工作项关联的工作池或工作队列。
工作池信息在工作项被排队后一直可用,直到工作项被同步取消。
工作队列信息仅在工作项处于队列中时可用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 static inline void set_work_data (struct work_struct *work, unsigned long data) { WARN_ON_ONCE(!work_pending(work)); atomic_long_set(&work->data, data | work_static(work)); }
set_work_pwq 设置工作项的工作池(pool_workqueue) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 static void set_work_pwq (struct work_struct *work, struct pool_workqueue *pwq, unsigned long flags) { set_work_data(work, (unsigned long )pwq | WORK_STRUCT_PENDING | WORK_STRUCT_PWQ | flags); }
insert_work 将一个工作项(work_struct)插入到工作池(pool_workqueue)的指定位置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 static void insert_work (struct pool_workqueue *pwq, struct work_struct *work, struct list_head *head, unsigned int extra_flags) { debug_work_activate(work); kasan_record_aux_stack(work); set_work_pwq(work, pwq, extra_flags); list_add_tail(&work->entry, head); get_pwq(pwq); }
wq_node_nr_active 用于确定工作队列(workqueue_struct)在指定 NUMA 节点上的 wq_node_nr_active 数据结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 static struct wq_node_nr_active *wq_node_nr_active (struct workqueue_struct *wq, int node) { if (!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND)) return NULL ; if (node == NUMA_NO_NODE) node = nr_node_ids; return wq->node_nr_active[node]; }
tryinc_node_nr_active 尝试增加 wq_node_nr_active 结构体中的活动计数(nr) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 static bool tryinc_node_nr_active (struct wq_node_nr_active *nna) { int max = READ_ONCE(nna->max); while (true ) { int old, tmp; old = atomic_read (&nna->nr); if (old >= max) return false ; tmp = atomic_cmpxchg_relaxed(&nna->nr, old, old + 1 ); if (tmp == old) return true ; } }
pwq_tryinc_nr_active 尝试增加指定工作队列(pool_workqueue,简称 pwq)的活动工作项计数(nr_active) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 static bool pwq_tryinc_nr_active (struct pool_workqueue *pwq, bool fill) { struct workqueue_struct *wq = struct worker_pool *pool = struct wq_node_nr_active *nna = bool obtained = false ; lockdep_assert_held(&pool->lock); if (!nna) { obtained = pwq->nr_active < READ_ONCE(wq->max_active); goto out; } if (unlikely(pwq->plugged)) return false ; if (!list_empty(&pwq->pending_node) && likely(!fill)) goto out; obtained = tryinc_node_nr_active(nna); if (obtained) goto out; raw_spin_lock(&nna->lock); if (list_empty(&pwq->pending_node)) list_add_tail(&pwq->pending_node, &nna->pending_pwqs); else if (likely(!fill)) goto out_unlock; smp_mb(); obtained = tryinc_node_nr_active(nna); if (obtained && likely(!fill)) list_del_init(&pwq->pending_node); out_unlock: raw_spin_unlock(&nna->lock); out: if (obtained) pwq->nr_active++; return obtained; }
__queue_work 工作队列添加工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 static void __queue_work(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct work_struct *work) { struct pool_workqueue *pwq ; struct worker_pool *last_pool , *pool ; unsigned int work_flags; unsigned int req_cpu = cpu; lockdep_assert_irqs_disabled(); if (unlikely(wq->flags & (__WQ_DESTROYING | __WQ_DRAINING) && WARN_ONCE(!is_chained_work(wq), "workqueue: cannot queue %ps on wq %s\n" , work->func, wq->name))) { return ; } rcu_read_lock(); retry: if (req_cpu == WORK_CPU_UNBOUND) { if (wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND) cpu = wq_select_unbound_cpu(raw_smp_processor_id()); else cpu = raw_smp_processor_id(); } pwq = rcu_dereference(*per_cpu_ptr(wq->cpu_pwq, cpu)); pool = pwq->pool; last_pool = get_work_pool(work); if (last_pool && last_pool != pool && !(wq->flags & __WQ_ORDERED)) { struct worker *worker ; raw_spin_lock(&last_pool->lock); worker = find_worker_executing_work(last_pool, work); if (worker && worker->current_pwq->wq == wq) { pwq = worker->current_pwq; pool = pwq->pool; WARN_ON_ONCE(pool != last_pool); } else { raw_spin_unlock(&last_pool->lock); raw_spin_lock(&pool->lock); } } else { raw_spin_lock(&pool->lock); } if (unlikely(!pwq->refcnt)) { if (wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND) { raw_spin_unlock(&pool->lock); cpu_relax(); goto retry; } WARN_ONCE(true , "workqueue: per-cpu pwq for %s on cpu%d has 0 refcnt" , wq->name, cpu); } trace_workqueue_queue_work(req_cpu, pwq, work); if (WARN_ON(!list_empty(&work->entry))) goto out; pwq->nr_in_flight[pwq->work_color]++; work_flags = work_color_to_flags(pwq->work_color); if (list_empty(&pwq->inactive_works) && pwq_tryinc_nr_active(pwq, false )) { if (list_empty(&pool->worklist)) pool->watchdog_ts = jiffies; trace_workqueue_activate_work(work); insert_work(pwq, work, &pool->worklist, work_flags); kick_pool(pool); } else { work_flags |= WORK_STRUCT_INACTIVE; insert_work(pwq, work, &pwq->inactive_works, work_flags); } out: raw_spin_unlock(&pool->lock); rcu_read_unlock(); }
__queue_delayed_work 工作队列添加延时工作 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 static void __queue_delayed_work(int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay) { struct timer_list *timer = struct work_struct *work = WARN_ON_ONCE(!wq); WARN_ON_ONCE(timer->function != delayed_work_timer_fn); WARN_ON_ONCE(timer_pending(timer)); WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&work->entry)); if (!delay) { __queue_work(cpu, wq, &dwork->work); return ; } WARN_ON_ONCE(cpu != WORK_CPU_UNBOUND && !cpu_online(cpu)); dwork->wq = wq; dwork->cpu = cpu; timer->expires = jiffies + delay; if (housekeeping_enabled(HK_TYPE_TIMER)) { cpu = smp_processor_id(); if (!housekeeping_test_cpu(cpu, HK_TYPE_TIMER)) cpu = housekeeping_any_cpu(HK_TYPE_TIMER); add_timer_on(timer, cpu); } else { if (likely(cpu == WORK_CPU_UNBOUND)) add_timer_global(timer); else add_timer_on(timer, cpu); } }
queue_delayed_work_on 延迟后对特定 CPU 上的工作进行排队 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 bool queue_delayed_work_on (int cpu, struct workqueue_struct *wq, struct delayed_work *dwork, unsigned long delay) { struct work_struct *work = bool ret = false ; unsigned long irq_flags; local_irq_save(irq_flags); if (!test_and_set_bit(WORK_STRUCT_PENDING_BIT, work_data_bits(work)) && !clear_pending_if_disabled(work)) { __queue_delayed_work(cpu, wq, dwork, delay); ret = true ; } local_irq_restore(irq_flags); return ret; } EXPORT_SYMBOL(queue_delayed_work_on);
wq_worker_sleeping 处理一个工作线程(worker)进入睡眠状态时的相关逻辑 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 void wq_worker_sleeping (struct task_struct *task) { struct worker *worker = struct worker_pool *pool ; if (worker->flags & WORKER_NOT_RUNNING) return ; pool = worker->pool; if (READ_ONCE(worker->sleeping)) return ; WRITE_ONCE(worker->sleeping, 1 ); raw_spin_lock_irq(&pool->lock); if (worker->flags & WORKER_NOT_RUNNING) { raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); return ; } pool->nr_running--; if (kick_pool(pool)) worker->current_pwq->stats[PWQ_STAT_CM_WAKEUP]++; raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pool->lock); }
wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_init 初始化并动态调整wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_us
wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_us:该阈值定义了工作队列(workqueue)子系统判定一个工作项(work item)为“CPU密集型”的时间上限。
其工作原理基于一个自适应的启发式算法:
CPU密集型判定: 在工作队列的执行逻辑中,若一个工作项在持有工作者池(worker pool)内部锁的情况下,其执行时间超过 wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_us 微秒,该工作项将被分类为CPU密集型,并可能触发调度器对其进行特殊处理,以避免抢占其他重要工作。
动态调整的必要性: 一个固定的时间阈值无法适应性能差异巨大的各种硬件平台。对于高性能处理器,10毫秒可能已是相当长的时间;而对于低性能微控制器,这可能是一个常规操作所需的时间。因此,必须根据当前系统的计算能力来动态设定此阈值。
基于BogoMIPS的性能估算: 该函数利用内核在早期启动阶段通过calibrate_delay()计算出的loops_per_jiffy全局变量,来估算一个非精确但具备参考价值的性能指标——BogoMIPS。BogoMIPS粗略地反映了CPU执行简单指令循环的速度。
阈值缩放(Scaling)算法: 函数设定一个10毫秒的基准阈值。若计算出的BogoMIPS值低于4000,则判定系统为低性能平台,并启动缩放算法。该算法将阈值与BogoMIPS值成反比进行放大(thresh * 4000 / bogo),但上限不超过1秒。此算法确保了在计算能力较低的硬件上,该阈值会被放宽,以避免错误的密集型任务判定。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 static void __init wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_init (void ) { unsigned long thresh; unsigned long bogo; pwq_release_worker = kthread_run_worker(0 , "pool_workqueue_release" ); BUG_ON(IS_ERR(pwq_release_worker)); if (wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_us != ULONG_MAX) return ; thresh = 10 * USEC_PER_MSEC; bogo = max_t (unsigned long , loops_per_jiffy / 500000 * HZ, 1 ); if (bogo < 4000 ) thresh = min_t (unsigned long , thresh * 4000 / bogo, USEC_PER_SEC); pr_debug("wq_cpu_intensive_thresh: lpj=%lu BogoMIPS=%lu thresh_us=%lu\n" , loops_per_jiffy, bogo, thresh); wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_us = thresh; }
workqueue_init 使工作队列子系统完全上线 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 void __init workqueue_init (void ) { struct workqueue_struct *wq ; struct worker_pool *pool ; int cpu, bkt; wq_cpu_intensive_thresh_init(); mutex_lock(&wq_pool_mutex); for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { for_each_bh_worker_pool(pool, cpu) pool->node = cpu_to_node(cpu); for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) pool->node = cpu_to_node(cpu); } list_for_each_entry(wq, &workqueues, list ) { WARN(init_rescuer(wq), "workqueue: failed to create early rescuer for %s" , wq->name); } mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_mutex); for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) for_each_bh_worker_pool(pool, cpu) BUG_ON(!create_worker(pool)); for_each_online_cpu(cpu) { for_each_cpu_worker_pool(pool, cpu) { pool->flags &= ~POOL_DISASSOCIATED; BUG_ON(!create_worker(pool)); } } hash_for_each(unbound_pool_hash, bkt, pool, hash_node) BUG_ON(!create_worker(pool)); wq_online = true ; }
init_pod_type 根据特定的物理拓扑关系对系统中的所有CPU进行分组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 static void __init init_pod_type (struct wq_pod_type *pt, bool (*cpus_share_pod)(int , int )) { int cur, pre, cpu, pod; pt->nr_pods = 0 ; pt->cpu_pod = kcalloc(nr_cpu_ids, sizeof (pt->cpu_pod[0 ]), GFP_KERNEL); BUG_ON(!pt->cpu_pod); for_each_possible_cpu(cur) { for_each_possible_cpu(pre) { if (pre >= cur) { pt->cpu_pod[cur] = pt->nr_pods++; break ; } if (cpus_share_pod(cur, pre)) { pt->cpu_pod[cur] = pt->cpu_pod[pre]; break ; } } } pt->pod_cpus = kcalloc(pt->nr_pods, sizeof (pt->pod_cpus[0 ]), GFP_KERNEL); pt->pod_node = kcalloc(pt->nr_pods, sizeof (pt->pod_node[0 ]), GFP_KERNEL); BUG_ON(!pt->pod_cpus || !pt->pod_node); for (pod = 0 ; pod < pt->nr_pods; pod++) BUG_ON(!zalloc_cpumask_var(&pt->pod_cpus[pod], GFP_KERNEL)); for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) { cpumask_set_cpu(cpu, pt->pod_cpus[pt->cpu_pod[cpu]]); pt->pod_node[pt->cpu_pod[cpu]] = cpu_to_node(cpu); } }
unbound_wq_update_pwq 专门用于处理非绑定(unbound)工作队列在CPU热插拔(hotplug)事件发生时的状态更新
当一个CPU被添加或移除时,系统中CPU的拓扑结构会发生变化。对于非绑定工作队列,其工作项(work item)可以在一组允许的CPU上执行。此函数的作用就是,在CPU变化后,重新计算和调整该工作队列在特定CPU上关联的 pool_workqueue (pwq) 结构,确保工作项能够被调度到符合最新CPU亲和性掩码(cpumask)的处理器池中,从而维持系统的高效运行。在像STM32H7这样通常不支持CPU热插拔的嵌入式系统上,这个函数在运行时可能永远不会被调用,但它是通用内核所必需的一部分。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 static void unbound_wq_update_pwq (struct workqueue_struct *wq, int cpu) { struct pool_workqueue *old_pwq =NULL , *pwq; struct workqueue_attrs *target_attrs ; lockdep_assert_held(&wq_pool_mutex); if (!(wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND) || wq->unbound_attrs->ordered) return ; target_attrs = unbound_wq_update_pwq_attrs_buf; copy_workqueue_attrs(target_attrs, wq->unbound_attrs); wqattrs_actualize_cpumask(target_attrs, wq_unbound_cpumask); wq_calc_pod_cpumask(target_attrs, cpu); if (wqattrs_equal(target_attrs, unbound_pwq(wq, cpu)->pool->attrs)) return ; pwq = alloc_unbound_pwq(wq, target_attrs); if (!pwq) { pr_warn("workqueue: allocation failed while updating CPU pod affinity of \"%s\"\n" , wq->name); goto use_dfl_pwq; } mutex_lock(&wq->mutex); old_pwq = install_unbound_pwq(wq, cpu, pwq); goto out_unlock; use_dfl_pwq: mutex_lock(&wq->mutex); pwq = unbound_pwq(wq, -1 ); raw_spin_lock_irq(&pwq->pool->lock); get_pwq(pwq); raw_spin_unlock_irq(&pwq->pool->lock); old_pwq = install_unbound_pwq(wq, cpu, pwq); out_unlock: mutex_unlock(&wq->mutex); put_pwq_unlocked(old_pwq); }
workqueue_init_topology 为非绑定工作队列初始化CPU “pod”(荚/分组) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 void __init workqueue_init_topology (void ) { struct workqueue_struct *wq ; int cpu; init_pod_type(&wq_pod_types[WQ_AFFN_CPU], cpus_dont_share); init_pod_type(&wq_pod_types[WQ_AFFN_SMT], cpus_share_smt); init_pod_type(&wq_pod_types[WQ_AFFN_CACHE], cpus_share_cache); init_pod_type(&wq_pod_types[WQ_AFFN_NUMA], cpus_share_numa); wq_topo_initialized = true ; mutex_lock(&wq_pool_mutex); list_for_each_entry(wq, &workqueues, list ) { for_each_online_cpu(cpu) unbound_wq_update_pwq(wq, cpu); if (wq->flags & WQ_UNBOUND) { mutex_lock(&wq->mutex); wq_update_node_max_active(wq, -1 ); mutex_unlock(&wq->mutex); } } mutex_unlock(&wq_pool_mutex); }